How to Build an AI Chatbot: how to build an ai chatbot for growth
Building an AI chatbot isn't just about plugging in some code and hoping for the best. It’s a deliberate process that starts with clear goals, moves to choosing the right tech—like LLMs and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)—and finishes with careful development, testing, and deployment. This guide is designed to take you beyond a simple FAQ bot and show you how to build a powerful tool that actually moves the needle for your business.
Why Building An AI Chatbot Is A Game Changer
Let's cut through the noise. For B2B and SaaS companies, creating a high-quality AI chatbot has graduated from a "nice-to-have" experiment to a core business strategy. We’ve all been frustrated by clunky, unhelpful bots from a few years ago. Today's tools are different. They're sophisticated enough to become a primary interface for your entire customer journey, doing far more than just spitting out canned answers.
The real goal here is to create a practical, high-ROI asset. When done right, a chatbot can:
- Automate and scale customer support, handling common questions instantly, 24/7.
- Qualify inbound leads with targeted questions, filtering the signal from the noise and even scheduling demos.
- Streamline internal workflows, from onboarding new hires to managing IT helpdesk tickets.
This guide gives you a clear roadmap to get there, laying out the actionable steps for planning, building, and deploying a chatbot that genuinely enhances how you operate.
The Shift From Novelty To Necessity
The numbers don't lie. This isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift in customer interaction. The chatbot market is growing at over 20% CAGR globally, ballooning from $7.76 billion to a projected $27.3 billion by 2030. For a B2B founder, this means a chatbot isn't just a UX tweak. It's about meeting a new customer expectation and plugging into a rapidly maturing tech infrastructure.
At the heart of this evolution is conversational AI, the technology that allows bots to grasp context, navigate complex dialogues, and actually get things done. Understanding this is key to creating the kind of natural, human-like interactions that build trust and keep users engaged.
To give you a bird's-eye view of the journey we're about to embark on, here's a high-level roadmap.
Roadmap to Your High-Performance AI Chatbot
| Stage | Primary Goal | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Planning & Strategy | Define clear business objectives and scope. | Identify use cases, define KPIs, and select the right tech stack (LLMs, RAG). |
| 2. Data & Development | Prepare knowledge bases and build the core bot. | Collect and clean data, set up vector databases, engineer prompts, and write application code. |
| 3. Integration & Testing | Connect the bot to your existing systems. | Integrate with CRM and support tools, conduct rigorous user testing, and evaluate performance. |
| 4. Deployment & Operations | Launch the chatbot and establish maintenance. | Deploy to production, monitor performance, and create SOPs for continuous improvement. |
This table maps out the entire lifecycle, ensuring we cover all the critical steps from initial concept to a fully operational, value-driving asset.
The entire process boils down to a simple, powerful framework.
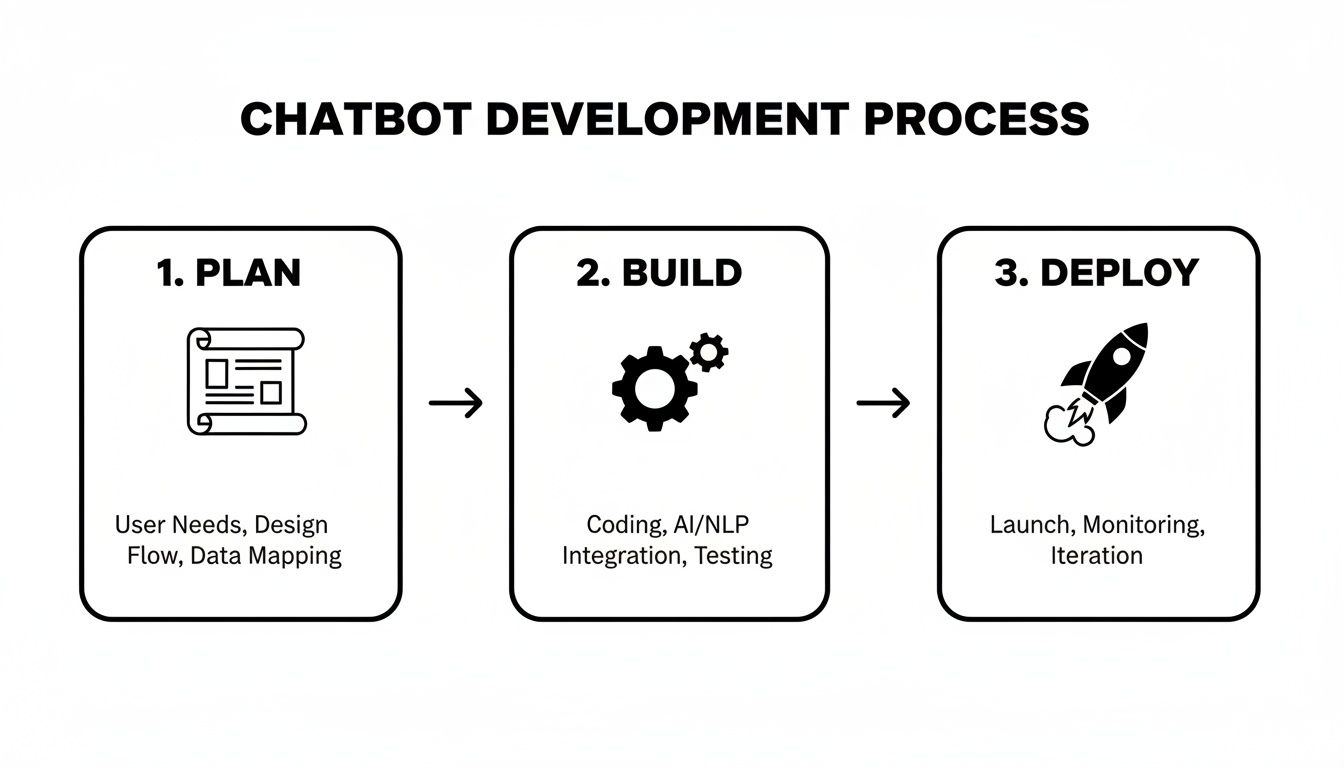
This three-stage flow—Plan, Build, Deploy—is the foundation of any successful chatbot project. It forces you to get the strategy right before a single line of code is written, which is where so many projects go wrong.
Laying the Foundation for a High-Performing Bot

Before you write a single line of code, the most critical decisions about your AI chatbot have already been made. It doesn't matter how powerful your LLM is or how slick your architecture is; if the bot doesn't have a clear purpose, it’s dead on arrival. This is the planning phase where you shift from a vague idea of "building a chatbot" to defining its precise, measurable impact on your business.
A great chatbot isn't just a friendly conversationalist—it's an automation engine. The real win here is designing for a tangible return on investment (ROI), not just for snappy dialogue. Your bot has to solve a genuine business problem, whether that's taking routine tasks off your sales team's plate or slashing customer wait times.
Don’t skip this part. Seriously. Without this strategic groundwork, you'll end up with a technically impressive toy that nobody uses or, worse, one that fails to move the needle on your key business metrics.
Define Your Primary Business Goal
First things first: what is the single most important job this bot will do? Trying to make it a jack-of-all-trades from the get-go is a classic mistake and a surefire path to mediocrity. Zero in on one specific, high-impact workflow that’s currently a bottleneck or a major time sink for your team.
For B2B and SaaS, some common starting points are:
- Automating Lead Qualification: Let the bot handle the initial screening questions and book meetings with qualified leads. This frees up your SDRs to focus on high-value conversations.
- Triaging Support Tickets: Have the bot automatically categorize incoming support requests and route them to the right team, cutting down on manual sorting and getting answers to customers faster.
- Empowering User Self-Service: Give customers a way to find answers to common questions about billing, features, or troubleshooting on their own, 24/7.
Pick one clear objective and build everything around it. This focus will be your north star for every decision that follows, from the data you collect to the prompts you write. Nail one workflow, and then you can think about expanding.
The goal is to build a chatbot that actually performs in an enterprise setting by designing for automation ROI, not just conversations. Chatbots can already complete roughly 30% of tasks done by today’s contact center staff, which shows just how deeply they can replace manual work when built correctly. In fact, data shows 43% of companies are investing in AI automation for support scalability, and 80% either use or plan to use AI-powered chatbots for customer service. If you want to dive deeper, you can explore more detailed chatbot statistics.
Map the Ideal User Journey
With your goal locked in, it’s time to walk in your user's shoes. This isn’t about scripting every possible conversational turn but about defining the key milestones and decision points in the interaction. A user journey map helps you visualize the flow from the user’s perspective, making sure it’s intuitive and gets them where they need to go.
For a lead qualification bot, the journey might look something like this:
- Initial Greeting: The bot pops up to welcome a visitor browsing your pricing page.
- Problem Identification: It asks what challenge the visitor is trying to solve with your product.
- Qualification Questions: The bot follows up with a few key questions about their company size, role, and maybe budget.
- Actionable Outcome: Based on the answers, it either books a demo directly on a sales rep's calendar or offers a relevant case study to download.
Mapping this out is invaluable for spotting potential friction points early on. It helps you design a bot that smoothly guides users toward the finish line and tells you exactly what information you need to collect at each step.
Gather Your Essential Data
The data you feed your bot is what makes it smart. There's no substitute for high-quality, relevant data; it's the single most important ingredient for an accurate and helpful AI. Start pulling together the raw materials that reflect real-world customer interactions and your company’s source-of-truth knowledge.
Your data repository should include things like:
- Past Support Tickets: Transcripts from tools like Zendesk or Intercom are gold. They show you the most common questions and how your best agents answer them.
- Sales Call Transcripts: If you use platforms like Gong or Chorus, those transcripts are a treasure trove of customer objections, feature questions, and buying signals.
- Knowledge Base Articles: Your existing help center, FAQs, and internal wikis are your official source of truth for product info and company policies.
This collection of data will become the knowledge base for your Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system. This is what allows your bot to provide answers grounded in your specific business context, not just generic web knowledge. The better your data, the smarter your bot—it’s that simple.
Choosing Your Tech Stack And Architecture

Alright, with a solid plan in place, it's time to get into the nuts and bolts. We need to make the core technical decisions that will bring your chatbot to life. This isn't just about picking shiny new tools; it's about architecting a system that works brilliantly today and can grow with you tomorrow.
The great news is you don't have to build an LLM from the ground up. The modern AI stack is incredibly modular. Think of yourself as an architect, selecting the best components and orchestrating them into a cohesive system that solves your unique business problem.
And the market for this is exploding. The generative AI chatbot market is projected to skyrocket from $10.83 billion to $35.68 billion between 2025 and 2029. This tells us one thing loud and clear: the game has shifted. B2B teams are now expected to build smart solutions on top of major foundation models like ChatGPT and Gemini, not train their own.
The Core Components of a Modern AI Chatbot
At the heart of any truly smart chatbot today, you'll find three concepts working in tandem: Large Language Models (LLMs), Embeddings, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Getting a handle on how these three interact is fundamental.
-
Large Language Models (LLMs): This is the brain of the operation. Think of models like GPT-4, Gemini, or Claude. They’re pre-trained on staggering amounts of text and can understand context, follow complex instructions, and generate remarkably human-like text.
-
Embeddings and Vector Databases: This is how you infuse the LLM with your specific company knowledge. An embedding model translates your documents—knowledge base articles, product specs, you name it—into numerical representations, or vectors. These are then stored in a specialized vector database built for lightning-fast semantic search.
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): RAG is the bridge that connects the LLM to your proprietary data. When a user asks a question, the system doesn't just pass it to the LLM. First, it searches your vector database for the most relevant information and then "augments" the LLM's prompt with that context. This is the secret to getting accurate answers grounded in your company's truth.
This RAG architecture is what separates the most effective business chatbots from the rest. It dramatically cuts down on "hallucinations" (when the AI makes things up) and ensures the bot provides answers based on your actual data, not just its general knowledge.
Pre-Built Platforms vs. Custom Development
One of the first forks in the road is deciding whether to go with a no-code/low-code platform or build a custom solution from scratch. There isn't a one-size-fits-all answer here. The right path really depends on your team's skills, timeline, budget, and how much control you need.
Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide which path makes the most sense for your team.
Comparing Chatbot Development Approaches
| Factor | No-Code/Low-Code Platforms | Custom Development |
|---|---|---|
| Speed to Market | Blazing fast—think days or weeks. | Slower and more methodical, often months. |
| Technical Skill | Minimal. Built for non-developers. | Requires a dedicated engineering team. |
| Customization | Limited to the platform's features. | Fully customizable. The sky's the limit. |
| Initial Cost | Lower, usually a monthly subscription. | Higher upfront development investment. |
| Scalability | Dependent on the platform's limits. | Built to your specific scaling needs. |
For a lot of B2B teams, a low-code platform hits the sweet spot. It gets you to market quickly while still offering enough flexibility to integrate with crucial systems like your CRM. You get to focus on the user experience and business logic instead of reinventing the wheel on core infrastructure.
Selecting The Right Large Language Model
The LLM you choose will directly influence your chatbot's performance, speed, and operating costs. The main players right now—OpenAI's GPT series, Google's Gemini, and Anthropic's Claude—each come with their own set of strengths.
Your LLM is the engine of your chatbot. Picking the right one isn't just a technical detail; it's a strategic decision that shapes the entire user experience. A model optimized for speed might be perfect for quick Q&A, while one with superior reasoning is better for complex, multi-step tasks.
Here's a quick rundown of the trade-offs to consider:
- Performance and Reasoning: For tasks that require deep analysis or complex logic, heavy-hitters like GPT-4 and Claude 3 Opus are the top contenders.
- Speed and Latency: When a near-instant response is critical for a real-time conversation, models like GPT-3.5 Turbo or Gemini 1.5 Flash offer a fantastic balance of speed and capability.
- Cost: This is a huge factor, especially as you scale. The smaller, faster models are significantly cheaper per token. My advice? Always start with a more cost-effective model and only upgrade if the use case absolutely demands more powerful reasoning.
To help you choose, check out this practical AI showdown between Claude and ChatGPT. It provides a head-to-head comparison that can clarify which model truly fits your needs.
Ultimately, the goal is to design an architecture that solves today's problems while being flexible enough for whatever comes next. Start with a focused use case, pick the right components for the job, and remember that many of the best AI chatbots for customer service prioritize reliability and accuracy over simply using the most powerful model on the market.
Development, Integration, and the Art of Prompt Engineering
Alright, you've got your architecture mapped out and your tech stack picked. Now comes the fun part: moving from blueprint to a real, working chatbot. This is where we stitch everything together—the code, the systems, and the subtle art of telling the AI exactly what to do.
Think of this phase less like building from scratch and more like a smart assembly job. We've got incredible frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex that provide the scaffolding. This lets you skip the grunt work and focus on the secret sauce: your unique business logic and the integrations that will actually save your team time.
Let's get our hands dirty and look at how to connect these pieces, and more importantly, how to get the AI to behave like a seasoned member of your team.
Bringing Your Chatbot to Life with Code
The heart of your chatbot is its ability to connect your private knowledge base to a powerful LLM. We do this using a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline. In simple terms, this setup forces the bot to find answers in your documents first, preventing it from just making things up based on its general internet training.
Here’s a practical, high-level Python snippet using LangChain to show you what this looks like. This code handles loading your documents, turning them into a searchable format (embeddings), and setting up the basic logic.
Import necessary libraries from LangChain and others
from langchain_community.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings, ChatOpenAI
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
1. Load your knowledge base documents
loader = DirectoryLoader('./your_knowledge_base_files/', glob="*.md")
docs = loader.load()
2. Split documents into smaller, manageable chunks
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter()
documents = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
3. Create embeddings and store them in a vector database (like FAISS)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vector = FAISS.from_documents(documents, embeddings)
retriever = vector.as_retriever()
4. Define the prompt template for the LLM
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("""Answer the following question based only on the provided context:
{context}
Question: {input}""")
5. Initialize the LLM and create the RAG chain
llm = ChatOpenAI()
document_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
retrieval_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, document_chain)
6. Ask a question!
response = retrieval_chain.invoke({"input": "What are your pricing plans?"})
print(response["answer"])
This code snippet is the engine. It’s what gives your bot its brain, connecting your data to the LLM with a clear set of instructions on how to use it.
The Make-or-Break Skill: Prompt Engineering
Getting a RAG pipeline working is just one part of the equation. The real magic—and what separates a mediocre bot from a great one—is prompt engineering. This is the craft of writing instructions that guide the LLM's behavior. A lazy prompt gets you a lazy bot. A carefully engineered prompt creates a true brand ambassador.
If you want to truly level up your chatbot, you have to get good at this. For a fantastic deep dive, check out A Practical Guide to Prompt Engineering. This is how you transform a generic AI into a helpful, on-brand assistant that people actually enjoy interacting with.
Crafting a Powerful System Prompt
Your most critical instruction is the system prompt. Think of it as the bot's constitution—the master set of rules defining its persona, its boundaries, and its primary goals.
A solid system prompt for a B2B chatbot needs to cover a few key areas:
- Persona Definition: "You are a friendly and professional support assistant for 'SaaSify Inc.' Your goal is to help users solve their problems quickly and accurately."
- Knowledge Scoping: "You must answer questions only using the information provided in the context. If the answer is not in the context, you must say, 'I'm sorry, I don't have that information. Would you like me to connect you with a support agent?'"
- Behavioral Rules: "Never make up information. Do not answer questions unrelated to SaaSify Inc. Keep your responses concise and formatted with bullet points when possible."
- Escalation Paths: "If a user expresses frustration or asks to speak with a human three times, offer to create a support ticket for them immediately."
A well-defined system prompt is your primary defense against AI "hallucinations" and off-brand interactions. It sets the guardrails that ensure every conversation is productive and aligns with your business goals, turning a powerful but unpredictable tool into a reliable one.
Integrating with Your Business Systems
A chatbot that just answers questions is useful. A chatbot that takes action is a game-changer. This is where integrations come in. True automation kicks in when your bot can talk to your CRM, helpdesk, and calendar tools.
We make this happen with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). Your bot's code can be written to make API calls to these external systems to get things done.
Real-World Integration Scenarios
- Lead Qualification with Salesforce: When a user's answers flag them as a hot lead, the bot can make an API call to Salesforce to create a new lead record, pre-filling it with the details from the chat.
- Support Ticketing with Zendesk: If the bot hits a wall, it can use the Zendesk API to create a support ticket, attaching the full conversation transcript. No more repeating information for the user.
- Scheduling Demos with Calendly: A qualified prospect wants a demo? The bot can check a sales rep's availability via the Calendly API, offer up a few time slots, and book the meeting on the spot.
These integrations transform your bot from a simple Q&A machine into a genuine AI agent that can handle complex, multi-step tasks across your entire tech stack. If you want to explore this idea further, you can learn how to build an AI agent that truly automates business processes. This is where you start seeing a massive return on your investment.
Getting Ready for Launch: Testing, Deployment, and Never-Ending Improvement

Think of launching your chatbot not as the finish line, but as the starting gun. A bot that sits static after launch is a depreciating asset. The real work—the work that separates a neat gimmick from an indispensable business tool—begins now.
This is where rigor meets reality. You need to put your creation through the wringer before it ever interacts with a real customer, be smart about how you roll it out, and then bake continuous improvement into your team's DNA. This is how you build a bot that not only works on day one but actually gets smarter and more valuable over time.
A Battle-Tested Testing Strategy
Before your bot goes live, you have to put it through its paces. A multi-layered testing plan is non-negotiable; each stage is designed to catch different kinds of problems, from broken logic to just plain awkward conversations. Trust me, skipping steps here is a recipe for a public-facing failure that can seriously damage user trust.
Your testing playbook should have three core phases:
-
Functional Testing: This is the nuts and bolts. Does the bot actually do the things it’s supposed to? We're talking about the core mechanics and integrations. You should have a simple checklist of its main jobs—capturing a lead, creating a support ticket, pulling an article from the knowledge base—and hammer on them one by one.
-
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Now it's time to bring in fresh eyes. Grab people who have had zero involvement in the build and give them real-world tasks, like "try to book a demo" or "find our refund policy." UAT is gold for finding those confusing conversational flows where the bot’s logic just doesn't line up with how real people think and talk.
-
Performance and Load Testing: So, how does your bot handle a crowd? Use tools to simulate a flood of concurrent users to see where things start to creak or break. This is absolutely critical if you expect traffic spikes from a marketing campaign. You need to know your architecture can scale without response times grinding to a halt.
The single biggest mistake I see teams make is only testing the "happy path" where the user does everything perfectly. The real world is messy. The most valuable insights come from trying to break the bot on purpose—ask it weird questions, give it nonsense, and switch topics abruptly. This is how you find the most glaring weaknesses.
Deploying Smarter, Not Harder
Once your bot has passed its final exams, it's go-time. But a "big bang" launch, where you flip a switch and it’s live for everyone, is asking for trouble. A more strategic, phased approach minimizes risk and lets you learn from a smaller, more controlled audience first.
Here are two go-to deployment models:
-
Phased Rollout: You could start by deploying the bot only on a few specific, lower-traffic pages of your site. Another common tactic is to enable it for a small slice of your user base, say 10%, and slowly dial that up as you gain confidence. This contains the blast radius if any unexpected issues sneak through.
-
Internal-First Launch (Dogfooding): This is my personal favorite. Release the bot internally to your own sales or support teams first. They are your most knowledgeable and most critical users. Having them use it for their actual day-to-day work is the ultimate stress test and a fantastic way to collect high-quality, unfiltered feedback.
The right strategy really depends on your risk tolerance and what the bot is for. If it’s a mission-critical support tool, a slower, more cautious rollout is always the smart play.
Building Your Continuous Improvement Loop
Deployment is just the beginning of the optimization cycle. Your AI chatbot is a data-generating machine, and your job is to turn that raw data into actionable improvements. This feedback loop is the engine that drives long-term value.
Your post-launch process should revolve around a few key activities:
-
Become a Student of Conversation Logs: Regularly dive into the transcripts of user-bot interactions. You're hunting for patterns—spots where users get stuck, have to rephrase a question three times, or just give up. These are bright red flags telling you something is off.
-
Hunt for Knowledge Gaps: Pay very close attention to questions the bot fumbled. Was it because the information isn't in your knowledge base, or did the RAG system just fail to find it? Every missed question is a perfect opportunity to expand and enrich your data sources.
-
Watch Your Escalation Rates: Keep a close eye on how often the bot needs to hand off a conversation to a human. If you see a high escalation rate around a specific topic, you've found a major weakness in the bot's training or prompt engineering for that use case. With Gartner predicting that chatbots will become the main customer service channel for 25% of organizations by 2027, getting these handoffs right is crucial.
-
Refine, Tweak, and Repeat: Based on everything you're learning, you should be constantly tweaking your system prompts, updating your knowledge base, and refining the conversational logic. This isn't a one-and-done fix; it's a perpetual process of fine-tuning. Every small adjustment adds up to a better user experience and a much higher ROI.
Got Questions? Let's Get Them Answered
Even with the best plan in hand, you're bound to have questions as you get ready to build. That's perfectly normal. We've compiled the most common questions we hear from B2B and SaaS teams just like yours, aiming to give you the straight answers you need to move forward.
Let's tackle those last few uncertainties so you can start building with confidence.
What's the Real Cost of Building a Custom AI Chatbot?
This is the big one, and the honest answer is: it depends. The investment can vary dramatically based on what you need. A simpler bot built on a low-code platform might only set you back a few thousand dollars to get started.
But if you're aiming for a sophisticated, LLM-powered assistant woven into your core systems, you should realistically budget anywhere from $15,000 to over $50,000.
The main things that will influence your final cost are:
- LLM API Usage: This is an ongoing operational cost. It’s based on how many requests your bot handles and which model you’re using.
- Workflow Complexity: The more systems you need to connect—think CRM, ERP, or your helpdesk—the more development time and cost it will take.
- Custom UI/UX: A unique, branded front-end experience will add to the budget compared to using an off-the-shelf interface.
- Data Hosting & Maintenance: Don't forget the recurring costs for things like vector databases and the servers that keep everything running smoothly.
How Long Will It Actually Take to Build?
The timeline really hinges on the path you take. If you use a pre-built platform, you could have a basic prototype up and running in a matter of weeks. It’s a great way to get started quickly.
For a fully custom, production-ready chatbot that’s deeply integrated with your business, a two-to-four-month timeline is much more realistic.
A project like that usually breaks down into a few key phases:
- Discovery & Planning: 2-4 weeks
- Development & Integration: 6-10 weeks
- Testing & Deployment: 2-4 weeks
My advice? Start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This approach gets a working version into the hands of real users much faster, allowing you to collect invaluable feedback that will shape the future of the project.
One of the biggest mistakes I see teams make is trying to build the "perfect" chatbot on the first go. Don't overengineer it. Nail one or two high-value workflows, see how users interact with it, and then iterate. Real-world feedback is gold.
What Are the Biggest Challenges I Should Watch Out For?
Knowing the potential pitfalls ahead of time can save you a world of headaches. When it comes to building an AI chatbot, a few common roadblocks tend to trip teams up.
Here’s what to keep an eye on:
- Poor Data Quality: Your chatbot is only as smart as the information you feed it. Inaccurate, outdated, or messy data is the single biggest reason why chatbots fail to perform and give frustratingly wrong answers.
- Unclear Scope: This is classic "scope creep." If you don't define a razor-sharp goal from the outset, your project can easily get bloated. You end up trying to solve everyone's problems at once and solving none of them well.
- Unnatural Conversations: This is a dead giveaway of poor prompt engineering. A bot that sounds robotic or can't follow a simple conversation creates a terrible user experience and ultimately pushes customers away.
- Forgetting Maintenance: A chatbot is a living tool, not a one-and-done project. It needs ongoing attention—monitoring conversation logs, analyzing performance, and regularly refreshing its knowledge base to stay sharp and effective.
Ready to build an AI chatbot that doesn't just answer questions, but actively automates workflows and drives growth for your business? At MakeAutomation, we specialize in creating and implementing AI solutions that get rid of manual work and help you scale. Book a consultation with us today and let's talk about how we can build a high-performing AI asset for you.