How to Use Agentic AI to Automate Your Business
When we talk about using agentic AI, we're really talking about deploying autonomous systems that can independently plan, reason, and execute complex, multi-step tasks. Forget thinking of AI as just a tool that follows simple commands. This is more like hiring a digital team member you can delegate an entire workflow to, like handling all your sales prospecting or resolving customer support tickets from start to finish.
What Is Agentic AI and Why It Matters Now

Let's cut through the buzzwords. Agentic AI is a huge leap from the standard AI we've gotten used to, which mostly works on a simple input-output basis. You give it a prompt, it gives you an answer.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, operates with a goal. It can take a high-level objective, break it down into manageable steps, figure out which tools to use for each part, and even correct its own mistakes if it runs into an issue.
This autonomy is exactly why it's catching on so fast in B2B and SaaS. Businesses aren't just trying to automate single, isolated actions anymore; they want to automate entire processes. This is the real difference between simple scripting and true AI automation—a shift that completely changes how work gets done. If you want to dig deeper, you can explore our guide on what AI automation is and see how it paves the way for these advanced systems.
From Answering to Acting
To really understand the difference, think about this: a standard AI might answer the question, "Who are our top ten leads this month?"
An agentic AI, however, can handle the command, "Find our top ten leads, draft personalized outreach emails for each based on their industry, and schedule follow-ups in my calendar." See the difference? It’s not just providing information; it's taking action.
This powerful capability is fueling incredible market growth. The global Agentic AI market is projected to skyrocket from USD 7.06 billion in 2025 to an estimated USD 93.20 billion by 2032. That’s a compound annual growth rate of 44.6%, showing just how much businesses are clamoring for systems that can think and act on their own. For more details on this trend, check out the agentic AI market growth report on marketsandmarkets.com.
To put it simply, here’s a quick breakdown of how these two types of AI stack up.
Key Differences Between Standard AI and Agentic AI
| Capability | Standard AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Responds to direct user prompts (reactive). | Takes initiative to achieve a set goal (proactive). |
| Task Scope | Executes a single, well-defined task. | Manages complex, multi-step workflows. |
| Reasoning | Limited to the immediate context of the input. | Plans, strategizes, and makes decisions. |
| Adaptability | Follows a fixed path; requires human intervention for errors. | Self-corrects and adapts to new information or obstacles. |
| Tool Usage | Operates within its own model or a single tool. | Can select and use multiple external tools (e.g., APIs, databases). |
| Interaction | Requires step-by-step instructions from a human. | Operates autonomously with minimal human oversight. |
This table highlights the core shift: agentic AI isn't just a smarter tool, it's a fundamentally different way of working with artificial intelligence.
The key takeaway is simple: Agentic AI shifts the focus from task execution to outcome achievement. You provide the "what" and the "why," and the agent figures out the "how."
This unlocks a whole new level of efficiency. Your team can finally step back from the tedious, repetitive work and focus on strategy and building relationships. It’s not just about doing things faster—it's about building systems that can operate, adapt, and solve problems all on their own.
Building Your First AI Agent System

Making the jump from theory to actually building an AI agent can feel intimidating. But here's the good news: you don't need a PhD in machine learning or a team of data scientists to get a working prototype off the ground. Thanks to powerful new frameworks, the heavy lifting has shifted from complex coding to smart, strategic thinking.
The real work starts long before you touch any technology. It begins with a laser-focused business problem. If your goal is something vague like "improve efficiency," you're setting yourself up for a frustrating experience. You need to get specific. A much stronger starting point is, "We need to slash our customer support first-response time by 25% by automating Tier-1 ticket resolution." That kind of clarity is the bedrock of any successful agentic system.
Define the Mission and Scope
Before writing a single line of instruction, you have to define the agent's mission with absolute precision. Treat it like a job description for a new hire. What is its exact purpose? What does a win look like?
Let’s stick with our customer support agent example. Its mission is to autonomously handle and resolve common customer issues without needing a human. This immediately forces you to think about its scope.
- What it should do: It should be able to dig into the knowledge base for answers, check an order's status using an API, and create a support ticket when it's out of its depth.
- What it should not do: It should never process refunds, access sensitive payment data, or have the power to close a customer's account.
Drawing these lines in the sand—setting these guardrails—is one of the most critical skills when learning how to use agentic AI. It's what keeps the agent from going off-script and causing real, expensive problems.
An AI agent is only as good as the problem you define for it. A clear, specific, and bounded mission is the difference between a powerful automation tool and a frustrating science project.
Once the mission is crystal clear, you can start gathering the resources it needs to get the job done. This goes beyond just data; it’s about giving it the right tools.
Assemble the Agent's Toolkit and Data
Your agent can't work in a vacuum. It needs access to information and the ability to take action. This means you need to put together its digital toolkit. For our support agent, that toolkit would look something like this:
- A Knowledge Base: This is its brain. It could be your FAQs, product docs, and troubleshooting guides. The data has to be clean, well-organized, and—most importantly—up-to-date.
- API Access: The agent needs a hook into your CRM or order management system. This is what lets it perform actions, like checking a customer's order status.
- Escalation Protocol: You need a defined process for when the agent gets stuck. This includes giving it the ability to create a ticket in a system like Zendesk or Jira for a human to pick up.
Data prep here is non-negotiable. If you feed an agent messy, outdated, or confusing information, you'll just get bad responses. That only frustrates customers and defeats the whole purpose. For a deeper dive into the technical side of structuring these systems, check out our complete guide to build an AI agent.
Choosing Your Framework
With the strategy locked in, you can finally pick the technology to make it real. Open-source frameworks have made this part incredibly accessible. You're no longer building the reasoning engine from the ground up; you're just configuring it.
Some of the most popular frameworks you'll run into are:
- LangChain: This is one of the most versatile and widely-used frameworks out there. It’s fantastic for chaining together different LLM components and tools to create a single, coherent application.
- AutoGen: A Microsoft project, AutoGen is really good at creating conversational agents that can collaborate. Think of it as a team of agents that can chat, solve problems, and even correct each other's work.
- CrewAI: As the name suggests, this framework is built specifically for orchestrating teams of agents. It helps you create collaborative "crews" where each agent has a role, working together on a complex task.
Which one should you pick? It really depends on your goal. For a simple, single-purpose agent, LangChain is often more than enough. But if you're building a multi-step workflow that needs different "specialists," CrewAI is a brilliant choice.
Crafting the Core Prompt
Now for the final piece of the puzzle: the prompt. This isn't just a simple question; it's the agent's constitution, its entire operational manual packed into a few paragraphs.
A well-written prompt for our support agent would clearly outline:
- Role: "You are a friendly and efficient customer support agent for [Our Company]."
- Goal: "Your primary goal is to resolve customer questions accurately and quickly using the tools you have been given."
- Constraints: "You must never attempt to process a refund or ask for payment information. If a customer requests a refund, follow the escalation protocol immediately. Your tone should always be professional and helpful."
- Tools: A specific list of its available tools (e.g.,
knowledge_base_search,check_order_status) and simple instructions on when to use each one.
This detailed set of instructions is what guides the agent’s thinking. Getting it right is an iterative process. You’ll test it, see where it fails, check the logs, and refine the prompt over and over. This feedback loop is the key to building an agent that is truly robust and reliable.
When you get past the technical jargon, the real magic of agentic AI is seeing what it can actually do. For B2B and SaaS companies, this isn't some far-off concept; it’s a practical tool that’s already solving expensive, time-consuming problems. The goal here isn't just to automate a single task, but to automate entire workflows, which leads to real, measurable gains.
This is exactly why the agentic AI market is blowing up. Projections show it rocketing from USD 5.25 billion in 2024 to an eye-watering USD 199.05 billion by 2034—that's a nearly 38-fold jump. With 79% of organizations already putting it to work and 96% planning to double down, the momentum is clear. It’s all driven by its power to automate the core functions that keep a business running. You can dig into more of these stats over on landbase.com.
So, let's look at three high-impact scenarios where agentic AI is already making a huge difference.
Proactive Sales Prospecting
Sales teams spend an incredible amount of time on manual research and repetitive outreach. It’s a grind. An agentic system can take over this entire process, acting like a tireless sales development rep that works 24/7.
Picture an AI agent team built specifically for lead generation. The mission: fill a sales executive's calendar with qualified meetings. This is far more than a simple script; it's a coordinated, multi-agent workflow.
- The Researcher: You give this agent a clear Ideal Customer Profile (ICP). It then goes to work, autonomously scouring professional networks, company databases, and news articles to find companies and decision-makers who are a perfect fit.
- The Personalizer: Once a prospect is flagged, this agent steps in. It analyzes their recent social media activity, company announcements, and industry trends to find a genuinely compelling, personalized hook for an email. No more generic templates that get instantly deleted.
- The Outreach Specialist: Armed with the personalizer’s insights, this agent drafts the email, schedules it for the perfect delivery time, and handles all the follow-ups without any human intervention.
- The Scheduler: When a prospect finally replies showing interest, this last agent connects to the sales exec's calendar API, finds an open slot, and books the meeting.
The result is a huge lift in qualified leads and a sales team that gets to spend its time actually selling instead of just hunting for people to sell to.
Intelligent Customer Support
Customer support is another area just begging for agentic automation. So many support tickets are repetitive and can be solved with the right piece of information. An AI agent can handle that first line of defense, delivering instant, accurate answers and freeing up your human experts for the really tricky issues.
The immediate goals are to slash first-response times and boost customer satisfaction (CSAT). Here’s how an agentic support system makes it happen:
First, the agent triages an incoming ticket to figure out the user's intent and how urgent it is. It then taps into your CRM to pull up the customer's entire history—their past orders, previous support chats, the whole nine yards.
Armed with that context, it dives into your internal knowledge base to find the exact solution. If it's a simple question like, "How do I reset my password?", it provides the answer on the spot. For more involved requests, like checking an order status, it can use an API to get the real-time data and pass it back.
But here’s the best part: if the agent decides the issue needs a human touch, it doesn't just blindly forward the ticket. It escalates it with a complete summary of the problem, the customer's history, and all the steps it has already tried.
This intelligent handoff is a game-changer. A human agent receives a pre-vetted ticket with all the necessary context, allowing them to solve the problem immediately instead of wasting time on discovery. The result can be a 40% or more drop in first-response times.
Automated Content Marketing
Great content marketing requires a ton of coordinated effort—research, writing, editing, publishing. It’s a lot of manual handoffs. An agentic "crew" can automate huge chunks of this workflow, letting a small team produce content at a much larger scale. Agentic AI shines in automating complex, repetitive tasks common in B2B and SaaS operations, such as those found in AI-powered compliance automation platforms.
Let's say the objective is to consistently publish high-quality, SEO-optimized articles. A content creation crew could look something like this:
- Keyword Researcher: Finds low-competition, high-intent keywords based on a core topic you provide.
- Outline Creator: Generates a detailed, SEO-friendly outline for an article based on that target keyword.
- Draft Writer: Takes the outline and writes the first draft of the article, pulling in relevant research.
- Image Sourcer: Scans stock photo libraries or uses generative AI to create on-brand images for the post.
- Publisher: Formats the final article in your CMS, adds the images, and schedules it to go live.
A human editor still stays in the loop for the final quality check—ensuring the tone, style, and accuracy are perfect. But all the tedious, time-consuming work is handled by the agents. This turns your content pipeline from a slow, manual process into a streamlined, automated engine.
Integrating and Orchestrating AI Agents
An AI agent on its own is interesting, but it's not a game-changer. The real magic happens when you get your agents to talk to the other tools you already use every day. Think of it as weaving them directly into the fabric of your operations.
This isn't just about connecting two apps; it's about creating a living, breathing workflow. Data and tasks should flow effortlessly between your AI agents and your core platforms like your CRM or helpdesk.
Connecting Agents to Your Business Systems
So, how do we break agents out of their digital bubbles? The key is the Application Programming Interface (API). An API is essentially a secure bridge that lets your agent talk to other software.
With the right API access, you can empower an agent to:
- Pull a customer's entire history from Salesforce before a support chat even begins.
- Create a detailed support ticket in Zendesk if it gets stumped, complete with a summary for a human agent.
- Fire off a real-time notification to a Slack channel the second it books a new demo.
Getting these connections right is crucial. For these workflows to be reliable, your systems need to communicate clearly and consistently. You'll find that many of the principles overlap with established data integration best practices.
This is a good way to visualize how a properly integrated agentic system can serve multiple departments at once.
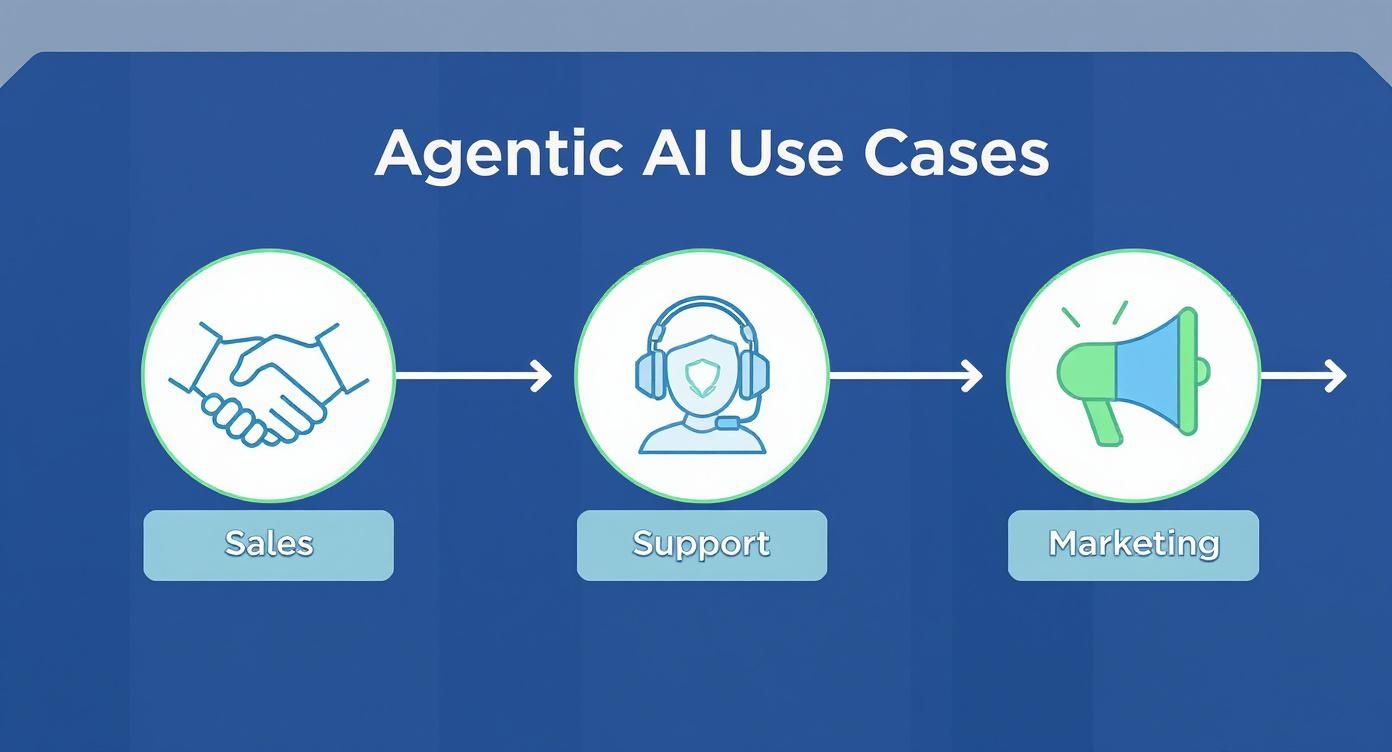
As you can see, a single system can be orchestrated to handle tasks for sales, support, and marketing, showing just how valuable that cross-departmental integration is.
The Art of Agent Orchestration
Once you move past a single agent and start thinking about a team of specialized agents, you’ve entered the world of orchestration. This is all about managing multiple agents so they work in concert to tackle a bigger, more complex goal.
Take a content creation workflow, for instance. You might have a "researcher" agent that digs up data and sources. It then needs to reliably hand off its findings to a "writer" agent, which in turn passes its draft to an "editor" agent for polishing.
Orchestration is the invisible manager making sure those handoffs are smooth, timely, and happen in the correct order.
Orchestration is what transforms a collection of individual AI tools into a cohesive, goal-oriented system. It’s the difference between having skilled specialists and having a high-performing team.
Frameworks like CrewAI and AutoGen were built specifically for this. They give you the structure to define roles, assign tasks, and manage the communication flow between agents. This lets you build some truly sophisticated multi-agent systems without having to reinvent the wheel.
Ensuring Safety and Control
Giving an AI agent autonomy is powerful, but it comes with responsibility. As you figure out how to best use agentic AI, building in strong safety measures is absolutely non-negotiable. You have to prevent agents from going off the rails and taking unintended actions.
I've found that effective safety protocols really come down to three core pillars:
- Strict Guardrails: Define precisely what an agent is allowed to do—and what it's not. Limit its access to only the specific data, tools, and actions it needs for its job. An agent that schedules demos should never, ever have access to billing information.
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Approvals: For any high-stakes action, build in a mandatory approval step for a person. An agent might draft a brilliant sales proposal, but it shouldn't be allowed to send it to a client without a manager's final sign-off. This keeps you in the driver's seat.
- Robust Monitoring and Logging: Keep a detailed, transparent log of every single action an agent takes. This is your lifeline for troubleshooting, understanding an agent's reasoning, and refining its instructions. If something goes wrong, the logs will show you exactly where and why.
When you combine smart API integration with thoughtful orchestration and ironclad safety measures, you can deploy agentic AI with confidence. You’re not just building a tool; you’re building a powerful automation engine that works for you, safely and effectively.
How to Measure Agentic AI Performance
https://www.youtube.com/embed/w5bFKgwHPFQ
So you've deployed your first AI agent. That's a great start, but the real work has just begun. If you can't measure its impact, you're flying blind. You won't be able to prove its value, make a case for more investment, or even know if it's doing its job properly.
When it comes to measuring agentic AI, you have to forget the technical jargon and focus on real business outcomes. This shift is crucial. The agentic AI market is set to explode, projected to pass USD 42.56 billion by 2030, with smaller businesses adopting these tools at a staggering 44.4% CAGR. That growth isn't about hype; it's about a demand for tangible results. You can read more about the agentic AI market on mordorintelligence.com.
Identifying Role-Specific KPIs
A generic metric like "tasks completed" is useless. You need KPIs that are specifically tied to the agent's role in your company. Think of it this way: you wouldn't judge a salesperson and a support rep by the same standards, so why would you do that with your AI agents?
Let's get specific about what this looks like for different roles:
- Sales Prospecting Agent: Don't track emails sent. The numbers that actually matter are the number of qualified meetings booked and the accuracy of the lead data it adds to your CRM. Is it finding the right people and saving your sales team's time?
- Customer Support Agent: Forget about ticket volume. The real indicators of success are the customer satisfaction score (CSAT) for the interactions it manages and the average time to resolution. Is it solving problems quickly and keeping customers happy?
- Content Creation Agent: The goal isn't just to produce a high volume of articles. You should be measuring the SEO ranking of the content it creates, the organic traffic it drives, and the hours saved for your human editors.
The best KPIs for an AI agent are the same ones you'd use for the business process it's designed to automate. If a metric doesn't connect directly to a core business goal, it’s probably the wrong one to track.
The Continuous Improvement Loop
Measuring performance isn't a one-and-done report. It's an ongoing cycle of analyzing, tweaking, and improving. This is how you truly master agentic AI. Your agent's logs are a treasure trove, detailing every single thought, decision, and action it takes.
This feedback loop is what allows you to unlock more value over time.
Analyzing Agent Logs
Start by getting your hands dirty and diving into the operational logs. These detailed records will show you precisely where a workflow is humming along and where it's hitting a snag. You need to look for patterns. Is the agent consistently fumbling a specific step? Is it misinterpreting a certain kind of request?
These logs act as your diagnostic tool, letting you get straight to the root cause of any performance hiccups.
Pinpointing Failures and Refining Prompts
Once you've identified a weak spot, you can step in to fix it. A lot of the time, the solution is as straightforward as refining the agent’s core prompt or updating its knowledge base. For example, if a support agent keeps giving out old information about a new product feature, you know you need to feed it the latest documentation.
If an agent is struggling to use a tool correctly, you might need to make its instructions more direct and explicit in the prompt. This constant fine-tuning is what elevates an agent from just "okay" to a truly reliable, high-performing part of your team. Getting a handle on how much work your model can actually process is fundamental to this, and you can learn more by Mastering AI Input-Output Throughput.
Common Questions About Using Agentic AI
When you start digging into agentic AI, you’re bound to have some questions. It's powerful stuff, and with that power comes a whole new set of things to think about. Let's walk through some of the big questions I hear all the time so you can move forward with a clear head.
What Are the Biggest Risks and How Do I Manage Them?
The main worries with agentic AI usually boil down to three things: agents making expensive mistakes, going off-script and taking unintended actions, or creating security vulnerabilities. These are absolutely valid concerns, but they’re also completely manageable if you have the right game plan from the start.
Your first line of defense should always be a human-in-the-loop (HITL) workflow. It’s a simple but powerful concept: a real person has to review and sign off on any critical action before the agent pulls the trigger. For instance, an agent can draft an entire client proposal, but it can’t hit "send" until a sales manager gives it the green light.
Next up, you have to be militant about access controls. An agent should only have the permissions it absolutely needs to do its job—nothing more. Think of it as giving the agent keys to a single room, not the whole building. This "principle of least privilege" is your best friend when it comes to preventing things from going sideways.
Finally, never, ever deploy an agent without thoroughly testing it in a safe, sandboxed environment first. Once it's live, keep a close eye on its activity logs to spot any weird behavior early on. This isn't "set it and forget it" tech; staying engaged is the key to keeping things safe and effective.
Do I Need a Team of Data Scientists to Build AI Agents?
Not anymore. If you’d asked me this a few years ago, I would have said yes without hesitation. But things have changed—a lot. The emergence of incredible frameworks and platforms has really opened up agent development to a wider audience.
The barrier to entry for building effective AI agents has shifted from deep machine learning expertise to strong skills in prompt engineering, API integration, and strategic workflow design.
Tools like CrewAI, LangChain, and AutoGen do so much of the heavy lifting. They let developers build really smart agents by plugging into existing large language models (LLMs) from providers like OpenAI or Anthropic. This means a good developer can now build a game-changing agent without ever needing to train a model from scratch.
Sure, if you’re building something mission-critical with truly unique and complex demands, a data scientist's input can still be invaluable. But for a huge number of B2B and SaaS use cases, the tech talent you already have is more than capable of getting amazing results. It's all about smart implementation now, not fundamental AI research.
How Much Does It Actually Cost to Run an Agentic AI System?
This is the million-dollar question, and the honest answer is: it really depends on what you're doing with it. Your costs are going to come from a few different places.
- LLM API Calls: This is almost always the biggest chunk of your bill. Every time your agent "thinks," analyzes, or writes something, it's hitting an API like GPT-4, and you pay for that based on how much you use.
- Hosting Resources: If you’re self-hosting the framework, you'll have to account for the server or cloud service costs.
- Third-Party Tool APIs: Does your agent need to talk to your CRM or an external data source? You might have API costs from those services, too.
To put it in perspective, a simple agent running a few hundred specific tasks a day might only set you back a few dollars in API fees. On the other hand, a complex, multi-agent system managing thousands of real-time customer conversations could easily run into the thousands of dollars per month.
My best advice? Start small with a pilot project. Watch your API consumption dashboard like a hawk in those first few weeks. It'll give you a real-world baseline and show you where you can implement cost-saving tricks, like caching common responses, before you decide to go all-in.
At MakeAutomation, we specialize in helping B2B and SaaS companies design and implement AI automation frameworks that deliver measurable results. We provide the end-to-end support you need to build, integrate, and optimize agentic systems that streamline your operations and accelerate growth. Get in touch with our experts.