8 Key Vendor Management Best Practices for 2025
In today's interconnected B2B and SaaS landscape, your vendors are more than just suppliers; they are extensions of your team and critical partners in your growth journey. The difference between moderate success and market leadership often lies in how effectively you manage these vital relationships. However, navigating the complexities of procurement, performance tracking, and risk mitigation can be a significant drain on resources if not handled correctly. This is where mastering vendor management best practices becomes not just a necessity, but a powerful competitive advantage.
Going beyond simple cost-cutting, a strategic approach transforms your supply chain into a well-oiled machine that fuels innovation, ensures resilience, and maximizes value. A well-executed vendor management strategy directly impacts your bottom line, enhances operational efficiency, and protects your brand reputation. For growth-stage companies and established enterprises alike, the ability to build and maintain strong, mutually beneficial vendor partnerships is a cornerstone of sustainable success.
This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to achieving precisely that. We move past generic advice to deliver actionable insights you can implement immediately. You will learn how to:
- Systematically evaluate and onboard the right partners.
- Segment vendors to apply the right level of management.
- Establish clear performance metrics and maintain accountability.
- Mitigate risks before they impact your operations.
- Leverage technology to streamline the entire process.
We will break down eight essential vendor management best practices designed to help you build a robust, efficient, and future-proof vendor ecosystem. Each section offers a detailed look at implementation steps, key metrics, and real-world examples to help you turn theory into tangible results and unlock your strategic advantage.
1. Comprehensive Vendor Assessment and Due Diligence
Effective vendor management begins long before a contract is signed. Comprehensive vendor assessment and due diligence is the foundational practice of thoroughly evaluating potential partners across multiple dimensions. This proactive process ensures that any new vendor aligns not only with your technical requirements but also with your organization's financial, operational, and security standards.
This initial deep dive prevents costly mismatches and mitigates future risks. By scrutinizing a vendor's financial stability, operational capabilities, security posture, and compliance status, you build a resilient and reliable supply chain. This step is crucial for any organization, especially in B2B and SaaS environments where third-party integrations can directly impact service delivery and data security.
How It Works
The process involves a structured, multi-departmental investigation into a potential vendor. Rather than a simple price comparison, it's a holistic analysis designed to verify a vendor's claims and assess potential risks.
- Financial Stability: Reviewing financial statements, credit ratings, and revenue history to ensure the vendor is a viable, long-term partner.
- Operational Capability: Assessing their infrastructure, quality control processes, and ability to scale. This often includes reference checks and performance history analysis.
- Security and Compliance: Auditing their data security protocols, privacy policies, and adherence to industry regulations (like GDPR, SOC 2, or HIPAA).
This infographic outlines the core pillars of a robust vendor assessment framework, showing how key criteria are organized.
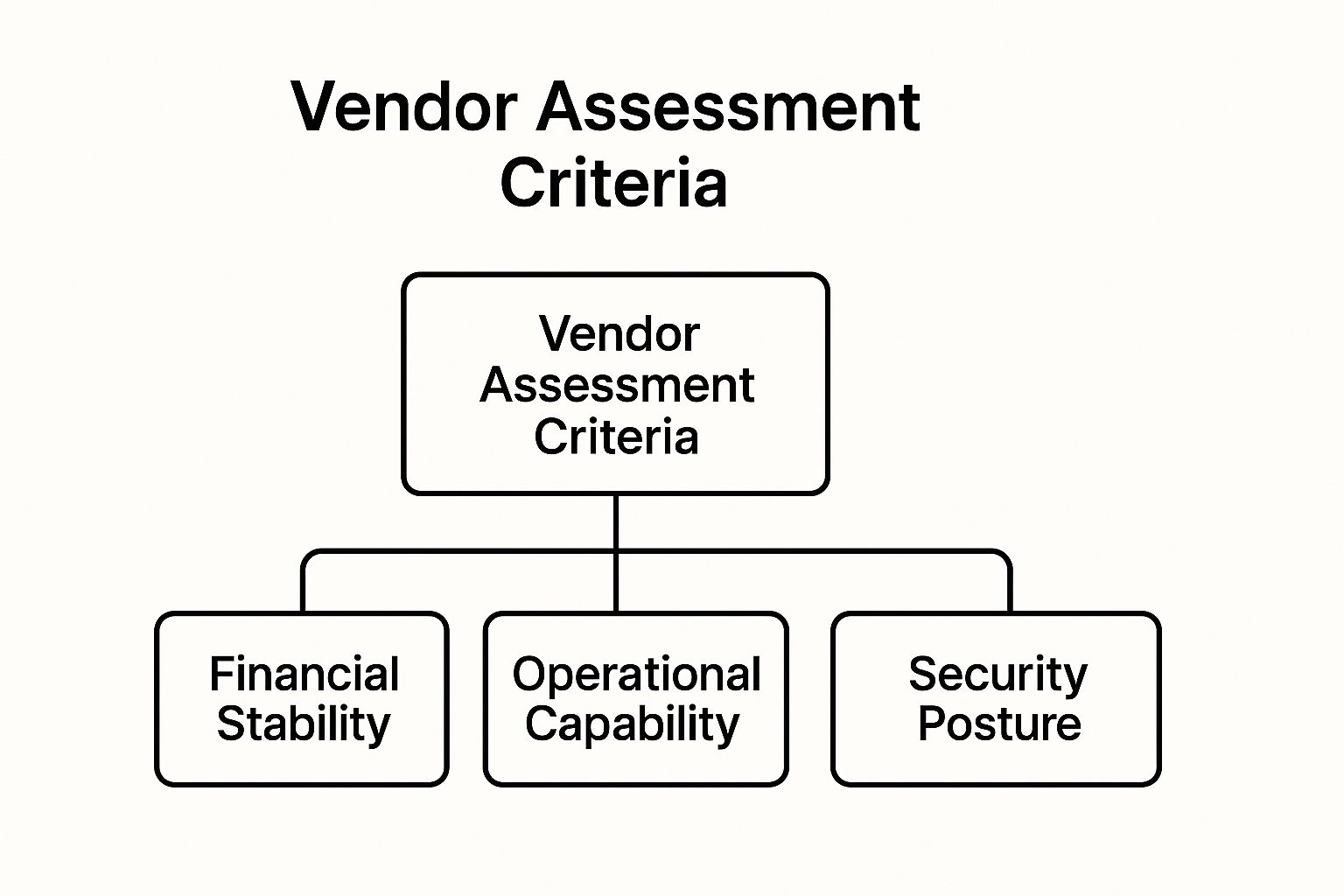
The hierarchy illustrates that a comprehensive assessment must balance financial health, operational delivery, and security rigor to be effective.
Real-World Example: Microsoft
Microsoft's Supplier Security and Privacy Assurance (SSPA) program is a prime example of this practice in action. Before onboarding, vendors handling sensitive data must complete a rigorous assessment covering data processing, security controls, and privacy standards. This ensures every link in their supply chain meets Microsoft's high bar for security, protecting both the company and its customers.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Standardize Your Approach: Develop a consistent vendor assessment template and scoring system to evaluate all potential partners objectively.
- Assemble a Cross-Functional Team: Involve stakeholders from IT, finance, legal, and the specific department that will use the vendor's service.
- Tailor Criteria to Risk: Create different tiers of assessment based on the vendor's criticality and access to sensitive data. A key software provider requires more scrutiny than an office supplies vendor.
- Leverage Technology: Use vendor management platforms to automate questionnaires, track responses, and maintain an updated profile for each vendor.
2. Strategic Vendor Segmentation and Relationship Management
Not all vendors are created equal, and managing them with a one-size-fits-all approach is inefficient and risky. Strategic vendor segmentation is the practice of categorizing suppliers based on their importance, spend, and risk profile. This allows you to allocate resources effectively and tailor your relationship management strategies to maximize value and mitigate potential disruptions.
This systematic approach moves beyond transactional interactions to build strategic partnerships where it matters most. By distinguishing between a critical software provider and a routine office supplier, you can focus high-touch, collaborative efforts on vendors that directly impact your core business operations. This is a cornerstone of mature vendor management best practices, ensuring that your most valuable partnerships receive the attention they deserve.
How It Works
This practice involves creating distinct tiers for your vendors, each with a predefined engagement model. The goal is to align the level of management oversight with the vendor's strategic value and associated risk, a methodology often highlighted in Gartner vendor management frameworks.
- Strategic Partners: High-spend, high-risk vendors critical to your operations. These relationships are managed collaboratively with executive oversight, joint business planning, and regular performance reviews.
- Preferred Suppliers: Important but less critical vendors. Management involves regular communication, performance monitoring, and established escalation paths.
- Transactional Vendors: Low-spend, low-risk suppliers providing easily replaceable goods or services. These are managed with automated, low-touch processes like e-procurement systems.
By tiering vendors, you create a clear roadmap for interaction, governance, and resource allocation across your entire supply chain.
Real-World Example: Apple
Apple's supply chain management is a masterclass in vendor segmentation. A strategic partner like Foxconn, responsible for assembling its flagship products, receives deeply integrated support, co-location of Apple engineers, and joint investment in new technologies. In contrast, suppliers of standard components are managed through more transactional, automated procurement systems. This tiered approach allows Apple to drive innovation with key partners while maintaining efficiency with thousands of other suppliers.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Establish Objective Criteria: Use a scorecard that combines spend volume, business impact, and risk factors (like data access or market scarcity) to segment vendors objectively.
- Define Engagement Models: Create a standard operating procedure (SOP) for each tier, outlining communication frequency, performance metrics, and governance requirements.
- Communicate Expectations Clearly: Inform vendors which tier they belong to and what that means for the relationship. This transparency builds trust and aligns expectations.
- Review and Re-evaluate Annually: Vendor criticality can change. Conduct an annual review to ensure your segmentation remains aligned with your current business strategy and market conditions.
3. Robust Contract Management and Governance
Once a vendor is selected, the contract becomes the central document governing the entire relationship. Robust contract management and governance is the practice of systematically managing the contract lifecycle, from negotiation and creation to execution, renewal, and termination. This discipline ensures that both parties adhere to their agreed-upon obligations, protecting your organization from risk and maximizing the value derived from the partnership.
This proactive approach transforms contracts from static legal documents into dynamic management tools. By actively monitoring performance against contractual terms, managing key dates, and controlling amendments, organizations can prevent value leakage, ensure compliance, and build stronger, more transparent vendor relationships. This is a critical component of effective vendor management best practices, as it directly links initial agreements to ongoing operational success.

How It Works
This practice involves establishing a clear framework and processes for the entire contract lifecycle, supported by defined roles and responsibilities. It moves beyond simple storage to active administration and strategic oversight, ensuring contracts deliver on their intended business objectives.
- Contract Standardization: Developing and using pre-approved templates for common agreements to ensure consistency, reduce legal review time, and include critical clauses.
- Performance Monitoring: Actively tracking vendor performance against the specific service level agreements (SLAs), key performance indicators (KPIs), and deliverables defined in the contract.
- Lifecycle Management: Systematically managing key contract milestones, such as renewal dates, termination notices, and price adjustment periods, to avoid auto-renewals of unfavorable terms or missed opportunities for renegotiation.
Real-World Example: IBM
IBM manages a vast global supply chain with over 100,000 vendor contracts. To handle this complexity, the company implemented a sophisticated contract lifecycle management (CLM) system. This platform centralizes all contracts, automates alerts for key dates, and provides analytics on vendor performance against contractual obligations. This robust governance allows IBM to enforce compliance, identify cost-saving opportunities, and manage risk across its entire supplier ecosystem effectively.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Implement Contract Management Software: Use a dedicated CLM platform to centralize contracts, automate notifications for renewals and milestones, and track amendments.
- Establish Clear Roles: Define who is responsible for contract negotiation, administration, performance monitoring, and sign-off to ensure clear accountability.
- Create Contract Playbooks: Develop internal guides with pre-approved negotiation positions, standard clauses, and acceptable fallback options to empower your team and maintain consistency.
- Conduct Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews of active contracts to ensure they still align with business needs and to identify opportunities for renegotiation or consolidation. To truly excel in this crucial area, a deep dive into mastering vendor contract management can provide the detailed strategies needed for success.
4. Continuous Performance Monitoring and Scorecarding
Effective vendor management is not a "set it and forget it" activity. Continuous performance monitoring and scorecarding is the practice of systematically tracking and evaluating vendor performance against predetermined metrics and Service Level Agreements (SLAs). This ongoing process ensures vendors consistently meet their contractual obligations and aligns their performance with your strategic business goals.
By establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), implementing monitoring systems, and conducting regular reviews, organizations can move from a reactive to a proactive vendor relationship model. This is one of the most critical vendor management best practices because it provides objective data to manage relationships, identify areas for improvement, and ensure you receive the value you are paying for, which is essential in B2B and SaaS partnerships where performance directly impacts your own service delivery.

How It Works
This practice transforms the vendor relationship into a transparent, data-driven partnership. It involves creating a structured framework for measurement and communication, which typically includes vendor scorecards that provide a clear, at-a-glance view of performance across different categories.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define clear, measurable, and relevant metrics that reflect what matters most to your business, such as delivery times, service uptime, quality defect rates, or customer support response times.
- Implement Monitoring Tools: Use vendor management software, internal dashboards, or other tools to collect performance data automatically and consistently.
- Conduct Regular Performance Reviews: Schedule regular meetings (e.g., quarterly business reviews) to discuss the scorecard results, celebrate successes, and collaboratively address any performance gaps.
This systematic approach ensures that both parties have a shared understanding of expectations and a clear picture of how the partnership is functioning.
Real-World Example: Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company's supplier scorecard system is a classic example of this best practice. Ford grades its suppliers on a "Q1" scorecard covering critical areas like quality, delivery, cost, and technology. To become a preferred supplier, vendors must meet and maintain high scores across these metrics. This system drives accountability and fosters continuous improvement throughout Ford's vast supply chain, ensuring every component meets its rigorous standards.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Align Metrics with Business Objectives: Ensure every KPI on your scorecard is directly tied to a specific business outcome or strategic goal.
- Involve Vendors in Metric Definition: Collaborate with vendors to define KPIs. This ensures the metrics are realistic and achievable, which fosters buy-in and a sense of shared ownership.
- Use Balanced Scorecards: Include a mix of quantitative (e.g., uptime percentage) and qualitative (e.g., innovation, collaboration) metrics to get a holistic view of vendor performance.
- Implement Performance Improvement Plans: For underperforming vendors, don't just terminate the contract. Work with them to create a formal, time-bound plan to address specific shortcomings.
5. Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Effective vendor management extends beyond initial assessments into the ongoing practice of identifying, analyzing, and neutralizing potential threats. A systematic approach to risk assessment and mitigation is vital for protecting your organization from the operational, financial, security, and reputational damage that a failing or compromised vendor can cause.
This practice involves proactively mapping out potential risks associated with each vendor relationship and developing clear strategies to address them. By anticipating issues before they arise, you can ensure business continuity, maintain compliance, and safeguard your assets. In B2B and SaaS contexts, where third-party services are often deeply integrated, this proactive stance on risk is a non-negotiable component of a mature vendor management program.
How It Works
This process involves creating a living framework for risk identification, quantification, and management. It moves beyond a one-time check to become a continuous cycle of monitoring and response, ensuring resilience against a dynamic threat landscape.
- Risk Identification: Cataloging potential risks across various domains, including operational (e.g., service disruptions), security (e.g., data breaches), financial (e.g., vendor bankruptcy), and compliance (e.g., regulatory fines).
- Risk Analysis and Prioritization: Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk. This allows you to prioritize high-impact, high-probability risks for immediate mitigation planning.
- Mitigation and Contingency Planning: Developing specific action plans to reduce the likelihood or impact of key risks. This includes creating contingency plans for worst-case scenarios, such as sudden vendor failure.
For organizations looking to deepen their expertise, mastering the nuances of building a robust third-party risk management program is an essential step toward achieving this level of operational resilience.
Real-World Example: Target
Following its massive 2013 data breach, which was traced back to a compromised HVAC vendor, Target completely overhauled its vendor risk management framework. The company implemented far stricter cybersecurity requirements for all third parties, mandating comprehensive security assessments and continuous monitoring. This incident became a landmark case, demonstrating the critical need for robust risk assessment that extends to every vendor, regardless of their primary function.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Develop Risk-Specific Templates: Create different risk assessment questionnaires for various vendor categories. The risks associated with a cloud hosting provider are vastly different from those of a marketing agency.
- Establish Clear Risk Thresholds: Define your organization's risk tolerance levels. Create clear escalation procedures for when a vendor's risk profile exceeds these predefined thresholds.
- Involve Vendors in Planning: Collaborate with critical vendors on risk mitigation and business continuity exercises. This fosters a partnership approach and ensures alignment in a crisis.
- Maintain Fourth-Party Visibility: Assess your vendors' own vendor management practices. Understanding the risks associated with their key subcontractors (your fourth parties) is crucial for a complete risk picture. This strategic oversight not only enhances security but can also lead to more efficient operations and reduce operational costs.
6. Technology-Enabled Vendor Management Platforms
Manual vendor management using spreadsheets and email is inefficient, prone to error, and simply does not scale. Adopting a technology-enabled vendor management platform centralizes and automates the entire vendor lifecycle, from onboarding and performance tracking to contract management and risk monitoring. This practice is a cornerstone of modern, strategic vendor management.
These integrated software solutions provide a single source of truth for all vendor-related data, eliminating information silos and enhancing cross-departmental collaboration. By leveraging workflow automation and analytics, organizations can move from reactive problem-solving to proactive, data-driven decision-making, significantly improving efficiency and reducing operational risk.
How It Works
A vendor management platform acts as a central hub for all interactions and documentation related to your suppliers. It standardizes processes that are often fragmented, ensuring consistency and compliance across the board.
- Centralized Onboarding: Automates the collection of essential vendor information, from tax forms to security questionnaires, through standardized digital workflows.
- Contract and Performance Management: Tracks key contract milestones, renewal dates, and service-level agreements (SLAs), while continuously monitoring vendor performance against predefined KPIs.
- Risk and Compliance Monitoring: Provides tools to assess, monitor, and mitigate vendor risks in real-time, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies.
This structured approach transforms vendor management from an administrative burden into a strategic function that drives value.
Real-World Example: Unilever
Unilever leverages SAP Ariba's supplier management solutions to manage its vast global network of suppliers. The platform provides end-to-end visibility and control over the procurement process, from sourcing and contracting to payment. This has enabled Unilever to streamline operations, enhance supplier collaboration, and ensure compliance with its sustainable sourcing goals, demonstrating how technology can support complex, large-scale vendor management best practices.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Conduct a Thorough Needs Analysis: Before selecting a platform, map your existing vendor management processes and identify key pain points and requirements.
- Prioritize Integration Capabilities: Ensure the chosen platform can seamlessly integrate with your existing enterprise systems, such as your ERP and accounting software.
- Plan for Change Management: Develop a comprehensive training and communication plan to ensure user adoption and a smooth transition. Learn more about implementing AI and automation for business to support this process.
- Start with a Pilot Program: Roll out the platform to a specific department or a small group of vendors first to identify and resolve issues before a full-scale launch.
7. Cross-Functional Vendor Governance Structure
Vendor management isn't a siloed task for the procurement team; it's a strategic organizational function. Establishing a cross-functional vendor governance structure breaks down departmental barriers, bringing together stakeholders from IT, legal, finance, and various business units to collectively oversee vendor relationships. This collaborative framework ensures that vendor-related decisions align with overarching business goals, rather than just the needs of a single department.
This integrated approach creates a unified front for managing risks, optimizing costs, and maximizing vendor value. By involving diverse perspectives, organizations can identify potential issues earlier, from security vulnerabilities spotted by IT to contractual risks flagged by legal. This practice is a cornerstone of mature vendor management best practices, transforming it from a tactical purchasing activity into a strategic, enterprise-wide discipline.
How It Works
A cross-functional governance structure formalizes collaboration through a dedicated committee or council. This body is responsible for setting vendor management policies, overseeing high-value contracts, and resolving escalations. It ensures that every stage of the vendor lifecycle, from selection to offboarding, is viewed through a holistic lens.
- Shared Accountability: The structure distributes responsibility, with IT assessing technical and security risks, finance evaluating financial viability, legal reviewing contracts, and business units confirming performance against objectives.
- Centralized Oversight: It provides a central point for decision-making on critical vendor issues, preventing inconsistent or conflicting approaches across the organization.
- Strategic Alignment: The committee ensures vendor activities directly support broader strategic initiatives, such as cost reduction, innovation, or a complete digital transformation across the company.
This collaborative model fosters proactive management, moving beyond reactive problem-solving to strategic partnership optimization.
Real-World Example: General Motors
General Motors (GM) utilizes a supplier council that exemplifies this practice. The council includes representatives from engineering, procurement, quality, and finance who meet regularly to discuss supplier performance, innovation opportunities, and strategic alignment. This cross-functional body ensures that supplier relationships are managed cohesively, balancing cost-effectiveness with the high-quality standards required for automotive manufacturing. By working together, these different functions can make more informed and strategic sourcing decisions that benefit the entire production chain.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Define Clear Roles and Authority: Document the specific responsibilities and decision-making power of each functional representative within the governance committee.
- Establish a Regular Cadence: Schedule recurring meetings (e.g., quarterly) to review vendor performance, discuss strategic goals, and address any ongoing issues.
- Standardize Collaboration Processes: Create and use shared templates for vendor reviews, risk assessments, and performance scorecards to ensure consistency.
- Use a Centralized Platform: Implement a vendor management system (VMS) to act as a single source of truth, facilitating seamless information sharing and collaboration among stakeholders.
8. Strategic Partnership Development and Innovation
Advanced vendor management best practices move beyond transactional relationships to cultivate strategic partnerships that foster mutual growth and innovation. This approach treats key suppliers not as replaceable commodities but as integral partners in value creation. It involves collaborative planning, shared risk-reward structures, and joint investments to achieve long-term competitive advantages that benefit both organizations.
This shift from a purely cost-driven model to a value-driven one unlocks new opportunities. By aligning with vendors at a strategic level, companies can co-develop innovative solutions, accelerate time-to-market, and build a more resilient and agile supply chain. This is especially critical in tech and SaaS, where collaboration on product development and technology integration is key to staying ahead.
How It Works
This practice involves identifying a select group of critical vendors and building deep, collaborative relationships with them. Instead of focusing solely on contract terms and SLAs, the emphasis is on joint business planning, open communication, and shared long-term objectives.
- Joint Goal Setting: Both parties work together to define mutual objectives, key performance indicators (KPIs), and a roadmap for innovation.
- Shared Risk and Reward: Contracts are structured to incentivize collaboration, with mechanisms for sharing both the profits from successful ventures and the risks of new initiatives.
- Executive-Level Engagement: Senior leaders from both organizations are actively involved, ensuring strategic alignment and providing top-down support for the partnership.
This collaborative framework transforms the traditional buyer-supplier dynamic into a powerful engine for innovation and mutual success.
Real-World Example: Tesla and Panasonic
The long-standing partnership between Tesla and Panasonic is a textbook case of strategic vendor collaboration. Instead of simply buying batteries off the shelf, the two companies jointly invested in the Gigafactory to co-develop and manufacture advanced battery cells. This deep integration allows them to rapidly innovate on battery technology, reduce costs, and scale production in a way neither could achieve alone, directly fueling Tesla's growth and market leadership.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
- Identify Strategic Partners: Segment your vendors and identify those with unique capabilities that are critical to your long-term strategy and competitive advantage.
- Establish a Governance Framework: Create a formal structure for the partnership with clear roles, responsibilities, and communication protocols, including regular executive business reviews.
- Define Mutual Objectives: Collaboratively develop a shared vision and a scorecard with metrics that track mutual value, not just supplier performance.
- Invest in the Relationship: Foster trust and transparency through open communication, joint problem-solving sessions, and a commitment to long-term success.
Vendor Management Best Practices Comparison
| Vendor Management Approach | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Vendor Assessment and Due Diligence | High | Significant expertise and time | Reduced risk, better vendor alignment | New vendor onboarding, risk mitigation | Objective evaluation, audit trail, risk reduction |
| Strategic Vendor Segmentation and Relationship Management | Medium to High | Ongoing assessment and maintenance | Optimized resource allocation, stronger relationships | Managing large vendor portfolios | Focused management, cost efficiency, strategic partnerships |
| Robust Contract Management and Governance | Medium to High | Investment in systems and training | Compliance, risk reduction, contract optimization | Contract lifecycle management | Standardization, visibility, proactive management |
| Continuous Performance Monitoring and Scorecarding | Medium | Data collection and analysis effort | Improved performance, early issue detection | Ongoing vendor performance management | Objective evaluation, continuous improvement |
| Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies | High | Continuous monitoring and analysis | Reduced disruptions, informed decisions | High-risk vendor portfolios | Proactive risk management, compliance support |
| Technology-Enabled Vendor Management Platforms | High | Upfront investment and training | Efficiency, real-time insights, streamlined workflows | Enterprise-wide vendor management | Automation, centralized data, analytics |
| Cross-Functional Vendor Governance Structure | Medium to High | Coordination across departments | Improved oversight, alignment, faster issue resolution | Complex organizations needing collaboration | Comprehensive view, reduced silos, risk oversight |
| Strategic Partnership Development and Innovation | High | Significant relationship investment | Innovation, competitive advantage, deep partnerships | Long-term, high-value vendor relationships | Drives innovation, shared risk/reward, mutual growth |
From Practice to Profit: Automating Your Vendor Management Success
We've explored a comprehensive roadmap for transforming your vendor relationships from simple transactions into powerful strategic alliances. Moving beyond mere cost management, the principles we've covered establish a foundation for resilience, innovation, and sustainable growth. Implementing these vendor management best practices is not just an operational upgrade; it's a fundamental shift in how your business creates value.
By embracing practices like comprehensive due diligence and strategic vendor segmentation, you ensure you're partnering with the right suppliers from the start. Robust contract management and continuous performance scorecarding provide the guardrails and visibility needed to maintain alignment and drive accountability. These elements work in concert to build a resilient operational backbone for your organization.
However, the true potential of this framework is realized when you move from reactive problem-solving to proactive value creation. This is where advanced strategies like establishing a cross-functional governance structure and pursuing strategic partnership development become critical. When you treat vendors as integral partners in innovation, you unlock new efficiencies, co-develop unique solutions, and build a competitive moat that is difficult for others to replicate.
The Bridge Between Strategy and Execution
The critical challenge is not understanding these principles, but implementing them consistently and at scale. A detailed vendor risk assessment is only valuable if it’s consistently applied. A performance scorecard loses its impact if the data is manually collected and infrequently updated. This is where the manual effort often becomes the bottleneck, preventing even the best-laid plans from achieving their full potential.
The journey from good to great in vendor management is paved with automation. Imagine a system where:
- Onboarding workflows automatically trigger due diligence checks, risk assessments, and contract reviews, ensuring no step is missed.
- Performance data from various systems is automatically aggregated into real-time dashboards and scorecards, eliminating manual data entry and providing instant insights.
- Contract renewal dates and key milestones trigger automated alerts to relevant stakeholders, preventing missed deadlines and enabling proactive negotiations.
- Risk monitoring systems continuously scan for compliance issues or negative sentiment, flagging potential problems before they escalate.
This level of integration transforms vendor management best practices from a checklist of tasks into a dynamic, self-optimizing engine for your business. It frees up your team from administrative burdens, allowing them to focus on strategic relationship-building, collaborative innovation, and maximizing the value derived from each partnership. Ultimately, a strategic and automated approach ensures your vendor ecosystem is not just a cost center but a significant driver of profitability and a core component of your competitive advantage.
Your Path to a Scalable Vendor Ecosystem
Mastering vendor management is a continuous journey of refinement and optimization. By implementing the strategies discussed, you are not just improving a single business function; you are strengthening the entire foundation upon which your company scales. Each optimized contract, mitigated risk, and innovative partnership contributes directly to your bottom line and your long-term market position.
The future of elite vendor management lies in leveraging technology to execute strategy flawlessly. By automating the tactical, you empower your team to excel at the strategic, ensuring that your network of suppliers becomes one of your most valuable and reliable assets for growth.
Ready to turn these best practices into an automated, scalable system? At MakeAutomation, we build custom AI and automation frameworks that streamline everything from vendor onboarding to performance tracking, eliminating manual work and giving you a real-time, 360-degree view of your vendor ecosystem. Visit MakeAutomation to discover how we can help you build a more efficient, resilient, and profitable supply chain.