What Is Business Operations Management Explained
Think of your business as a massive ship charting a course toward its goals. Business operations management is the engine room—that complex, vital hub below deck where people, processes, and technology work in concert to power the entire journey.
If that engine room isn't running smoothly, the ship slows, drifts off course, or grinds to a halt.
The Engine Room of Your Business

At its heart, business operations management is all about turning resources—like labor, materials, and software—into valuable goods or services as efficiently as possible. It's the strategic function dedicated to designing, managing, and constantly improving the systems that create and deliver what your company sells.
The real goal here is to make sure every part of the business works together seamlessly, resources aren't wasted, and customers get exactly what they expect, every single time.
Why Operations Management Is A Strategic Asset
Strong operations management is far more than just "keeping the lights on." It’s a genuine competitive advantage. When your operations are finely tuned, you can deliver better products, faster, and at a lower cost than anyone else in your space. This has a direct impact on both your top and bottom lines, fueling revenue while protecting your profit margins.
A solid operations strategy boils down to a few core objectives:
- Boosting Efficiency: Cutting out waste—whether it's wasted time, money, or materials—to accomplish more with less.
- Ensuring Quality: Putting controls and standards in place to make sure your products and services are consistently reliable.
- Improving Productivity: Refining workflows so your teams can create more value without getting bogged down or burning out.
- Driving Profitability: Making a clear connection between operational improvements and financial health, ensuring every efficiency gain strengthens the business.
Business operations management is the bridge between a company's big-picture vision and its daily reality. It's what turns abstract goals into the concrete, repeatable actions that build real value.
The table below breaks down the foundational pillars that make up a strong operations framework.
Core Pillars Of Business Operations Management
| Pillar | Primary Goal | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Process Design & Optimization | Create efficient, repeatable workflows | Mapping current processes, identifying bottlenecks, redesigning for better flow, and implementing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). |
| Resource & Capacity Planning | Match resources (people, equipment, budget) with demand | Forecasting future needs, scheduling staff and production, managing inventory levels, and allocating budgets effectively. |
| Supply Chain Management | Ensure a smooth flow of goods from supplier to customer | Sourcing raw materials, managing vendor relationships, overseeing logistics and distribution, and handling inventory control. |
| Quality Control & Assurance | Guarantee products and services meet set standards | Setting quality benchmarks, conducting inspections and testing, implementing feedback loops, and managing process improvements. |
| Technology & Systems Integration | Use tools to automate, track, and improve operations | Implementing ERP or CRM systems, adopting automation tools, managing data analytics platforms, and ensuring systems communicate. |
Each pillar supports the others, creating a robust structure that allows the entire business to function cohesively and effectively.
A Rapidly Growing Field
In a world that seems to change by the minute, the ability to adapt and execute flawlessly has never been more important. As companies invest heavily in digital tools, operations management has become a central focus for driving efficiency.
The global Operations Management System (OMS) market was valued at around $25 billion in 2023. It's projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12% through 2028, hitting an estimated $45 billion. You can read more on this market growth from Market Report Analytics. This surge shows just how critical a well-oiled operational machine has become to building a successful, lasting business.
What Operations Teams Actually Do
To get a real feel for business operations management, you have to look beyond the textbook definition and see what these teams do day-to-day. They’re the ones in the engine room, handling the distinct, interconnected functions that create value, keep things stable, and push the business forward.
Each function tackles a specific part of the journey from raw inputs to finished outputs. The goal is always to make the entire system efficient, reliable, and perfectly in sync with what the company is trying to achieve.
Designing the Blueprint for Success
First up is process design and management. Before anything gets built or delivered, an operations manager has to map out the entire workflow. This is the architectural phase—figuring out how tasks flow from one stage to the next and finding the most direct path.
A manufacturer might design an assembly line. A SaaS company, on the other hand, would map the customer onboarding journey, from the moment a user signs up to when they're a pro. Good design gets rid of bottlenecks, cuts out wasted effort, and builds a system you can repeat and scale. To get this right, you need clear guidelines, which is why we created a guide on what is process documentation.
Managing the Flow of Resources
Next, there's supply chain management. This isn't just for businesses with warehouses and trucks; every company has a supply chain. It's all about managing the entire journey of your resources, from where they start to where they end up with the customer.
A software company's "supply chain" might include cloud providers like AWS or Azure, third-party APIs they rely on, and the digital tools the team uses every day. The whole point is to keep everything flowing without interruption. This means picking the right vendors, handling contracts, and managing inventory (even digital assets). A single break in this chain can stop the entire business cold.
Ensuring Excellence and Consistency
Quality assurance and control is another non-negotiable function. It’s one thing to be efficient, but what you produce has to meet a consistent standard of excellence. This is where you set the benchmarks for quality and build the systems to make sure you're hitting them.
- For a physical product: This means inspections, material testing, and tracking defects.
- For a SaaS product: This looks like rigorous bug testing, user acceptance testing (UAT), and keeping a close eye on app performance to deliver a smooth user experience.
Quality assurance isn't just about catching mistakes before they reach the customer. It's about building a process that stops errors from happening in the first place, which is fundamental to protecting your brand and keeping customers happy.
Planning for Today and Tomorrow
Finally, capacity and resource planning is all about balancing what you have with what your customers need. Operations managers are always asking, "Do we have enough people, tech, and money to meet demand—both right now and down the road?" It’s a constant forecasting and scheduling act.
For a B2B service agency, this means making sure there are enough project managers to handle the current client load without burning them out or over-hiring and wasting money. When you get capacity planning right, you can scale smoothly without hitting those frustrating, unexpected roadblocks.
Measuring What Matters in Your Operations
You can have the most elegant processes in the world, but if you aren't measuring their performance, you're just flying blind. At its heart, effective business operations management runs on data. To find out if your engine is really humming, you have to connect your core workflows to the key performance indicators (KPIs) that tell you what’s actually happening.
This isn’t about chasing vanity metrics. It’s about understanding the story your numbers are telling about operational health. Good data lets you stop guessing and start knowing, so you can make targeted fixes that deliver real results.
Linking Processes to Performance Metrics
Every critical process in your business has a pulse, and KPIs are how you measure it. Whether you're a manufacturer watching an assembly line or a SaaS company monitoring user engagement, the principle holds true. You need to pinpoint the workflows that create value and then pair them with metrics that measure their speed, quality, and efficiency.
For instance, a classic workflow in many B2B companies is the Order-to-Cash (O2C) cycle. This process map covers every single step from the moment a customer places an order to the second your company gets paid. A slow or clunky O2C cycle is a direct hit to your cash flow and customer happiness.
On the other hand, a SaaS business can live or die by its Customer Onboarding process. A confusing, frustrating onboarding experience is a recipe for high churn. A smooth one, however, sets the stage for a long and loyal customer relationship. Each of these processes has specific KPIs that act as its vital signs.
You can think of operations as a continuous flow where one function feeds directly into the next, as shown below.
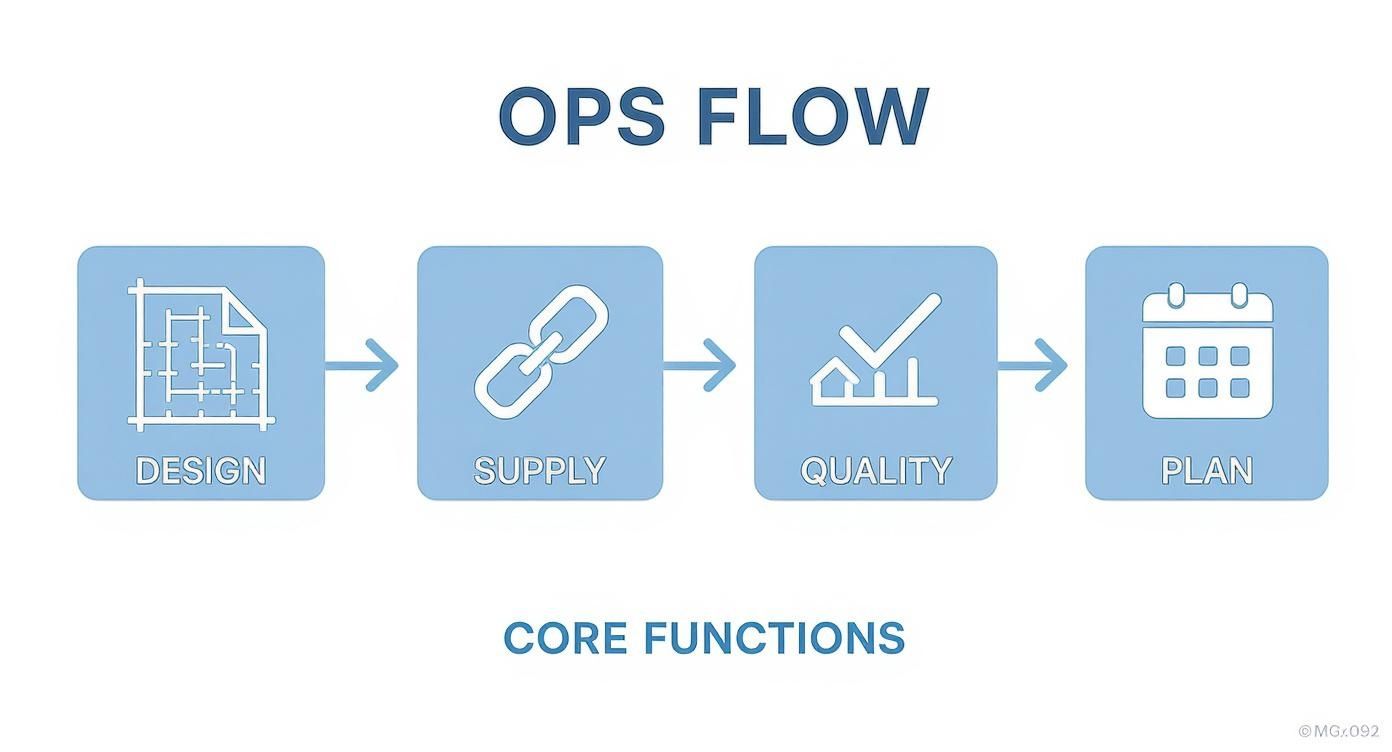
This visual drives home the point that operations isn't a collection of separate tasks. It's an interconnected system where the output of one stage becomes the input for the next.
Common Operational Processes and Their KPIs
So, let's get practical and break down a few essential processes and the metrics that keep them in check. Getting a handle on these connections is your first real step toward building a data-driven operational machine.
Here are a few examples you'll find in almost any business:
-
Customer Support & Service: This is your front line for keeping customers happy and loyal. How well it runs is non-negotiable.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): What percentage of customer problems get solved in the very first phone call, email, or chat? A high FCR means your team is knowledgeable and empowered, which saves everyone time and frustration.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Usually gathered from a quick survey ("How'd we do today?"), CSAT gives you direct, unfiltered feedback on the quality of each interaction.
-
Product Fulfillment & Delivery: This applies whether you're shipping physical boxes or delivering a digital service. It all comes down to how quickly and accurately you keep your promises.
- Cycle Time: This is the total clock time it takes to get something done from start to finish. For an e-commerce store, it's the time from "place order" to "delivered." For a software team, it might be the time from a feature request to its launch.
- Order Accuracy Rate: A simple but powerful metric. What percentage of orders go out the door without a single mistake? Low accuracy creates costly returns and erodes the trust you've built with your customers.
Key Takeaway: KPIs aren't just numbers to report in a meeting. They are diagnostic tools. A sinking CSAT score might tell you it's time for better training, while a creeping cycle time could be pointing to a hidden bottleneck in your workflow.
For a deeper dive into boosting team efficiency, looking into time tracking best practices can offer some valuable, concrete strategies.
The table below pulls these ideas together, showing how the right metrics can give you a crystal-clear view into the health of your core business functions.
Essential Operations KPIs And Their Business Impact
| Operational Process | Key KPI | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Onboarding | Time to Value (TTV) | How quickly a new customer gets to the "aha!" moment and sees the real benefit of your product. A short TTV is crucial for stopping early churn. |
| Sales Pipeline | Lead Conversion Rate | The percentage of potential customers (leads) who actually become paying customers. This number is a direct reflection of how effective your sales process is. |
| Manufacturing/Production | Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | A powerful metric that combines equipment uptime, performance speed, and quality output. It tells you how much of your production time is genuinely productive. |
| Inventory Management | Inventory Turnover | How many times your business sells and replaces its entire stock of inventory in a given period. A high turnover means sales are strong and you aren't wasting money on storage. |
Ultimately, these KPIs give you the feedback loop you need to continuously fine-tune your operations, ensuring the entire business is running as smoothly and profitably as possible.
Technology and Tools Powering Modern Operations
Let's be honest, modern business operations don't run on spreadsheets anymore. At least, the effective ones don't. Today, a sophisticated tech stack is the real engine driving operations, turning what used to be a reactive, problem-solving department into a strategic, forward-thinking powerhouse.
The right technology is a force multiplier. It gives teams the ability to spot challenges before they become problems, automate the tedious tasks that drain everyone's time, and jump on opportunities with surprising speed. These tools don't just make old processes faster; they unlock entirely new ways of working by providing clear data and the power to act on it.
Foundational Systems: The Central Nervous System
Every modern operation is built on a few core software platforms that act as the company's central nervous system. These systems are designed to collect, process, and share information, making sure everyone is working from the same playbook.
Two platforms are absolutely non-negotiable here:
-
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): You can think of an ERP as the business’s master database. It pulls everything—finance, supply chain, manufacturing, HR—into a single, unified system. For a manufacturer using an ERP like NetSuite, it tracks every bolt and widget from raw material to finished product, giving a complete picture of the entire production line.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): A CRM is mission control for anything and everything customer-related. Platforms like Salesforce bring all customer data into one place, tracking every interaction from the first sales call to ongoing support tickets. For a B2B SaaS company, a CRM is the lifeblood for managing sales pipelines and keeping a pulse on customer health.
The dashboard in the image above is a perfect example of what a good CRM provides—a clean, visual overview of sales activity and performance. This kind of centralized view lets leaders spot trends, balance team workloads, and forecast revenue with far greater confidence.
The Rise of Automation and Artificial Intelligence
If ERPs and CRMs are the foundation, then automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are the jet fuel. These technologies are fundamentally changing the game, shifting operations from just managing processes to actively predicting and improving them. Automation takes on the repetitive, rule-based work, freeing up your team for the kind of strategic thinking that actually moves the needle.
And this isn't some far-off trend; it's happening right now. By 2025, an estimated 67% of businesses will be using business process automation for better end-to-end visibility. On top of that, 86% of executives are already planning to invest in AI specifically to cut costs.
AI doesn’t just do what you tell it to; it learns from your data to make smarter suggestions. It can analyze past sales to predict future demand, flag a potential supply chain delay before it cripples production, or even route a support ticket to the one agent who knows how to solve that exact problem.
For a great example of this in action, see how the right document workflow software can eliminate manual bottlenecks.
Practical Applications in B2B and SaaS
This is where the rubber meets the road. Seeing these tools in action makes their value crystal clear.
-
Predictive Maintenance: A cloud services provider uses AI to constantly monitor its server performance. The system can predict when a piece of hardware is about to fail, letting the ops team schedule maintenance during quiet hours and avoid a catastrophic outage. That's a huge win.
-
Automated Ticket Routing: A SaaS company can connect an automation tool to its support inbox. The system reads each new ticket, identifies keywords like "billing," "bug," or "feature request," and instantly assigns it to the right team. No more manual triage, just faster resolutions.
Choosing the right tools is crucial for building an operational framework that can grow with you. If you're looking to bring automation into your core processes, our guide to the 12 best workflow automation tools is a fantastic place to start.
Navigating Common Operations Challenges
Even the smoothest-running business hits a few bumps in the road. The true measure of a solid operations strategy isn't about avoiding problems altogether—that's impossible. It's about having the foresight and agility to handle them when they inevitably pop up, especially during periods of rapid growth or unexpected market shifts.
Think of an operations manager as a master juggler. They’re constantly balancing the need to cut costs without sacrificing quality, scale up processes to meet a sudden flood of demand, and adapt to new tech or a competitor's latest move. Just knowing these problems exist isn't enough; you need practical, real-world strategies to tackle them head-on.
This problem-solving mindset is what builds a resilient company—one that doesn't just survive turbulence but actually learns and gets stronger from it.
Controlling Costs Without Compromising Quality
One of the oldest tug-of-wars in business is the budget. The pressure to trim operational expenses is constant. But if you cut corners in the wrong places, product quality plummets, and you risk damaging your brand's reputation and losing customer trust. The goal here is to be leaner, not cheaper.
This is where the principles of lean management really shine. The main idea is to systematically hunt down and eliminate "waste"—which is anything that uses up resources without adding any real value for the customer.
Here’s how you can put that into action:
- Map Your Value Stream: Get a whiteboard and visually chart out a process from start to finish. You’ll be surprised at how quickly you can spot bottlenecks, redundant steps, and pointless delays.
- Adopt a "Just-in-Time" (JIT) Mindset: For businesses dealing with physical goods, this is a game-changer. JIT minimizes warehousing costs by having materials arrive precisely when they’re needed for production, not a moment sooner.
- Empower Your Team: The people on the front lines often see the inefficiencies first. Encourage them to find and suggest small, continuous improvements—a concept the Japanese call kaizen.
This approach ensures that when you do cut costs, it's because you've become genuinely more efficient, not because you've started to short-change your customers.
Scaling Processes During Rapid Growth
Explosive growth is a fantastic problem to have, but it's still a problem. The workflows that were perfect for a 10-person startup will completely buckle under the pressure of a 100-person company. Manual tasks become overwhelming, communication gets messy, and consistency goes right out the window.
The fix? Design your operations to be scalable from day one. That means ditching rigid, manual systems in favor of flexible, modular frameworks. A crucial first step is to document every important workflow. Our guide on how to write standard operating procedures is a great place to start building a playbook that can grow with you.
Don't wait for a process to break before you fix it. Proactive operations management anticipates future strain and builds the infrastructure to handle it before it becomes a crisis.
Investing in modular, cloud-based software is also key. Modern tools for project management, CRM, and automation can easily scale their capacity up or down as you need them. This keeps you from getting locked into an expensive, oversized system or quickly outgrowing a smaller one. It's this flexibility that lets your operational backbone expand right alongside your business goals.
Your Top Operations Management Questions, Answered
When you start digging into business operations, a few common questions always seem to pop up. How is this different from project management? Does it even apply to my small business? What does a great ops manager actually do?
Let's clear the air and tackle these head-on. Think of this as the practical FAQ you've been looking for.
Business Operations vs. Project Management
This is probably the biggest point of confusion, and it's an important one to get right. While they’re often intertwined, operations and projects serve two totally different purposes.
Business operations is all about managing the ongoing, repeatable processes that keep the lights on. In contrast, project management deals with temporary initiatives that have a defined beginning and end.
Operations are about the daily grind—the cyclical work that has to happen for the business to function. A project is a one-off effort to create something new or change something significant. Once it's done, it's done.
- Operations Example: Managing the daily customer support queue to hit your service level agreements (SLAs). This never really stops; it's a core function.
- Project Example: Rolling out a brand-new CRM system company-wide. It has a specific timeline, a budget, and a goal. When the CRM is live, the project ends.
A simple way to think about it: Projects often build or improve the systems that the operations team will then run indefinitely.
How Operations Management Works in a Small Business
You don’t have to be a Fortune 500 company to put good operations management to work. In fact, for a small business, getting these principles right early on is the secret to scaling without everything falling apart.
Start simple. Grab a whiteboard and map out your most critical workflows. How does a new lead turn into a paying customer? What happens after they sign up? Just visualizing this process is often enough to spot glaring inefficiencies or steps that don't make sense.
From there, create some basic Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). This doesn't need to be a dusty, 100-page manual. A simple checklist in a shared Google Doc for recurring tasks can work wonders for consistency. Finally, lean on affordable tools—think Trello for organizing tasks or the free version of HubSpot CRM to get your customer data in order.
What Makes a Great Operations Manager?
A truly effective operations manager is a rare breed—they need to be just as comfortable digging into a spreadsheet as they are motivating a team. They're the glue that holds different parts of the company together, making sure the big-picture strategy actually gets done day-to-day.
Here are the non-negotiable skills:
- Analytical Skills: The ability to look at data and see the story behind the numbers. They can spot trends and diagnose problems before they become catastrophes.
- Problem-Solving: A natural talent for breaking down complex issues, finding the root cause, and, most importantly, implementing a real solution that sticks.
- Communication: They have to speak the language of sales, marketing, product, and finance—and get them all rowing in the same direction. Clarity is everything.
- Strategic Thinking: It’s not just about putting out fires. A great ops leader can connect today's tasks to the company's long-term goals, ensuring the daily hustle is moving the business forward.
At the end of the day, the best operations managers are masters of both systems and people.
At MakeAutomation, we specialize in transforming your core processes into efficient, scalable systems. We help B2B and SaaS businesses implement the AI and automation frameworks needed to eliminate manual work and accelerate growth. Optimize your operations with MakeAutomation today.