7 Quality Assurance Best Practices for AI & SaaS in 2025
In the competitive sphere of B2B SaaS and AI-driven automation, conventional quality assurance falls short. To deliver the flawless, reliable user experiences that drive customer retention and scalable growth, organizations must implement advanced strategies. These strategies must be tailored to the unique complexities of interconnected, intelligent systems where a minor glitch in an automated workflow can lead to significant business disruption. Standard testing protocols are simply insufficient for managing the dynamic nature of AI models and the intricate dependencies within SaaS platforms.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to seven critical quality assurance best practices designed for modern technological stacks. We move beyond generic advice to offer actionable insights specifically for optimizing AI-powered processes and SaaS environments. By applying these techniques, you can effectively mitigate risks, improve product reliability, and ensure your automated systems perform exactly as intended. These are not just theoretical concepts; they are practical, field-tested approaches that directly contribute to operational efficiency and a stronger bottom line.
You will learn how to:
- Integrate quality checks earlier in the development lifecycle to prevent costly rework.
- Prioritize testing efforts based on genuine business risks.
- Develop a smart test automation strategy that maximizes ROI.
- Foster a culture of shared quality ownership across teams.
Each best practice is broken down into specific implementation details and practical examples, providing a clear roadmap for enhancing your quality assurance framework. These methods are foundational for building robust, scalable systems that support sustainable business growth and deliver consistent value to your customers.
1. Shift-Left Testing
Shift-left testing is a foundational quality assurance best practice that integrates testing into the earliest stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Instead of treating QA as a final gate before release, this approach "shifts" testing activities to the left, embedding them within the requirements, design, and coding phases. The core principle is to prevent defects rather than just finding them late in the process.
This proactive strategy significantly reduces the cost and complexity of fixing bugs. A defect identified during the coding phase is exponentially cheaper and faster to resolve than one discovered after deployment. By involving QA expertise early, teams can clarify requirements, identify architectural flaws, and build quality directly into the product from day one.

Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
For AI-driven B2B and SaaS platforms, where automation workflows are complex and data integrity is paramount, a late-stage bug can cause significant disruption, from failed lead generation pipelines to inaccurate analytics. Shift-left testing ensures that the logic underpinning these automations is sound from its inception, fostering greater reliability and user trust.
Consider tech giants like Google and Microsoft. Google's culture of mandatory code reviews and extensive unit testing is a prime example of shifting left. Similarly, Microsoft's integration of continuous testing within its Azure DevOps ecosystem empowers developers to validate their code constantly, preventing flawed features from progressing.
Key Insight: Shift-left is not about making developers solely responsible for testing. It's about creating a collaborative culture where quality is a shared responsibility across the entire product team, from product managers to developers and QA engineers.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Implementing shift-left testing requires a strategic, phased approach. Here’s how to get started:
- Introduce Static Analysis: Integrate static code analysis tools (e.g., SonarQube, ESLint) directly into the developer's Integrated Development Environment (IDE). These tools automatically scan code for potential bugs, security vulnerabilities, and stylistic errors as it's being written, providing immediate feedback.
- Enforce Code Reviews and Quality Gates: Establish a mandatory peer-review process for all new code. Use automated quality gates in your continuous integration (CI) pipeline that block code from being merged if it doesn't meet predefined standards for test coverage or code quality.
- Empower Developers with Unit Testing: Train developers in testing methodologies like Test-Driven Development (TDD). Provide them with robust frameworks and tools to write effective unit tests, ensuring that individual components of your B2B/SaaS application function correctly in isolation before they are integrated.
2. Risk-Based Testing
Risk-based testing (RBT) is a strategic quality assurance best practice that prioritizes testing activities based on the probability and potential business impact of failures. Instead of aiming for exhaustive test coverage across an entire application, RBT allocates the majority of testing resources to the areas of highest risk, ensuring critical functionalities are rigorously validated.
This methodology forces teams to think critically about what could go wrong and what matters most to the business and its users. By focusing effort where it counts, RBT maximizes the effectiveness of the testing process, delivering the highest return on the QA investment while accelerating time-to-market.

Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
For AI-powered B2B and SaaS platforms, where downtime in core workflows can translate directly to lost revenue, risk-based testing is essential. A minor bug in a settings page is an inconvenience; a failure in the automated payment processing or data integration API is a catastrophe. RBT provides a logical framework for dedicating resources to protect these mission-critical functions.
Consider the financial services industry. A banking application team uses RBT to heavily prioritize testing payment processing and transaction security over cosmetic UI elements. Similarly, an e-commerce platform like Amazon focuses immense testing effort on its checkout and payment gateway flows, as any failure here has a direct and immediate financial impact, while a bug in the "recommended products" algorithm, though important, carries a lower immediate risk.
Key Insight: Risk-based testing transforms QA from a checklist activity into a strategic business function. It aligns testing priorities directly with business objectives, ensuring that quality assurance efforts protect the most valuable aspects of the product.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Implementing risk-based testing requires collaboration between technical and business teams. Here’s a practical way to begin:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment Workshop: Bring together product managers, business stakeholders, developers, and QA engineers to identify potential risks. For each feature, evaluate two key metrics: the likelihood of a defect occurring and the business impact if it does. This creates a risk matrix to guide priorities.
- Prioritize Test Cases Based on Risk Score: Assign a risk score to each application module or user story. High-risk areas (e.g., payment processing, user authentication) should receive comprehensive testing, including exploratory, negative, and security testing. Low-risk areas may only require basic smoke tests or sanity checks.
- Use Historical Data to Refine Assessments: Analyze past bug reports, production incidents, and customer support tickets. This historical data provides objective evidence of which application areas are most prone to defects, allowing you to refine your risk assessments and focus your testing where it has been needed most in the past.
3. Test Automation Strategy
A comprehensive test automation strategy is a strategic plan that defines how automated testing will be designed, implemented, managed, and scaled. Far more than just selecting tools, this quality assurance best practice outlines everything from which test cases to automate first, to the design of the testing framework, to how results are measured and maintained. The goal is to create a sustainable, scalable automation practice that delivers a clear return on investment.
This structured approach transforms automated testing from a sporadic, tactical activity into a strategic asset. It ensures that automation efforts align directly with business objectives, focusing on high-risk, high-value areas of the application. By establishing clear guidelines and standards, a well-defined strategy prevents the creation of brittle, hard-to-maintain tests, which is a common failure point for automation initiatives.
The following summary box highlights the typical impact of a well-executed test automation strategy on key performance metrics.
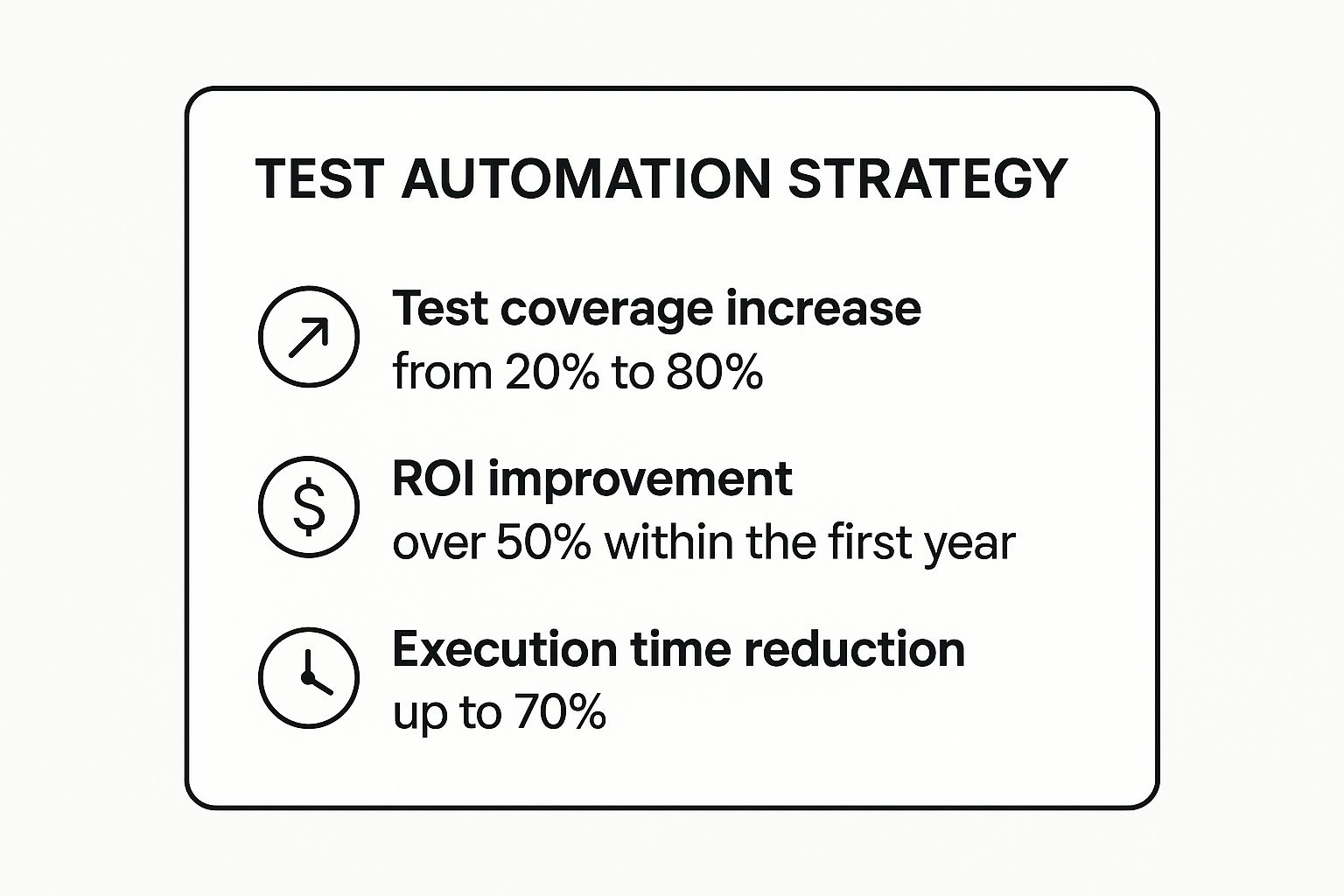
These metrics illustrate how a formal strategy can dramatically boost efficiency and test coverage while providing a significant financial return.
Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
For AI-powered B2B and SaaS platforms, where complex workflows and data-driven features are core to the user experience, manual testing alone is unsustainable. A robust test automation strategy is crucial for ensuring rapid, reliable release cycles. It allows teams to validate critical user journeys, such as customer onboarding or complex data processing pipelines, with every code change, catching regressions before they impact users.
Spotify is a prime example, achieving over 80% automated test coverage to support its continuous delivery model. Similarly, LinkedIn built a sophisticated in-house automation framework capable of running thousands of tests daily, ensuring platform stability despite frequent updates. These companies prove that a strategic approach to automation is a prerequisite for scaling quality. For a deeper understanding of how modern automation works, you can learn more about intelligent automation on makeautomation.co.
Key Insight: A test automation strategy is not just a technical document. It’s a business plan for quality that aligns engineering efforts with product goals, ensuring that automation investment yields tangible benefits in speed, reliability, and cost savings.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Implementing a successful test automation strategy requires careful planning and a phased rollout. Here’s a blueprint to get started:
- Prioritize Based on Value and Stability: Begin by identifying and automating test cases that are both critical to the business and stable. Focus on core functionalities like user authentication, checkout processes, or key report generation. Use the test automation pyramid, popularized by Mike Cohn, as a guide: build a large base of fast unit tests, a smaller layer of integration tests, and a minimal number of slow, end-to-end UI tests.
- Select Appropriate Tools and Frameworks: Choose automation tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing technology stack and CI/CD pipeline (e.g., Selenium for web UI, Cypress for modern web apps, Postman/Rest-Assured for APIs). Design a scalable and maintainable test framework that promotes code reuse, separates test data from test logic, and provides clear reporting.
- Establish Clear Governance and Metrics: Create and document clear automation standards and guidelines for the entire team. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track success, such as test execution time, percentage of automated test coverage, and the number of defects caught by automation. Regularly review these metrics to refine your strategy and demonstrate ROI.
4. Continuous Testing
Continuous testing is the practice of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release. This approach extends beyond simple test automation by integrating testing into every stage of the DevOps lifecycle, from code commit to production monitoring. It creates a nonstop quality feedback loop that validates code changes instantly and automatically.
The core goal is to make testing a seamless and ongoing activity rather than a distinct phase. By running tests continuously, teams can detect and address issues as soon as they are introduced. This is one of the most critical quality assurance best practices for maintaining development velocity without sacrificing stability, allowing for faster and more reliable deployments.
Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
For AI-driven B2B/SaaS platforms, the pace of innovation is a key competitive advantage. Continuous testing enables rapid iteration by providing the confidence to deploy changes frequently. In a complex system where a minor code change could impact a critical lead nurturing workflow or an analytics dashboard, this immediate validation is non-negotiable. It ensures that new features and bug fixes enhance the product without introducing regressions.
Tech leaders like Netflix and Amazon exemplify the power of continuous testing. Netflix's robust deployment pipeline runs a battery of tests at multiple stages, ensuring that any of their thousands of daily changes don't disrupt the user experience. Similarly, Amazon's legendary continuous deployment model relies heavily on automated quality checks at every step, allowing them to release code to production every few seconds with high confidence.
Key Insight: Continuous testing is not just about running tests more often. It's about a fundamental shift to using automated testing as a tool for risk assessment, providing real-time insights into whether a software release candidate is fit for purpose.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Embedding continuous testing into your workflow requires a well-orchestrated CI/CD pipeline and a strategic approach to test execution. Here’s how to begin:
- Establish Fast Feedback Loops: Structure your test suites to run the fastest and most critical tests first (e.g., static analysis, unit tests). This ensures developers get immediate feedback within minutes of a commit, before longer-running integration or end-to-end tests are triggered.
- Implement Quality Gates: Define clear, automated quality gates at key stages of your pipeline. For example, a gate could prevent code from being merged if unit test coverage drops below 85% or if any critical security vulnerabilities are detected, automatically enforcing your quality standards.
- Leverage Parallel Execution: Configure your CI/CD tool (like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or CircleCI) to run tests in parallel. This dramatically reduces the total time required for test execution, keeping your pipeline fast and efficient even as your test suite grows.
5. Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing is a dynamic and unscripted quality assurance best practice that champions the tester's cognitive engagement, freedom, and responsibility. Unlike rigid, pre-scripted test cases, this approach combines test design, execution, learning, and analysis into a continuous, real-time feedback loop. Testers act like detectives, using their curiosity and expertise to investigate the software, uncover its behavior, and discover defects that automated scripts would likely miss.
The power of this method lies in its adaptability. As testers interact with the application, they learn more about its strengths, weaknesses, and unexpected behaviors. This new knowledge immediately informs their next actions, allowing them to probe deeper into high-risk areas and explore complex user workflows organically. It's a method that values human intellect and intuition over rote execution.
Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
For complex AI-driven B2B and SaaS platforms, where user journeys can be non-linear and automation workflows have countless permutations, scripted testing alone is insufficient. Exploratory testing excels at identifying usability flaws, logical inconsistencies, and edge-case bugs in features like lead scoring algorithms or automated onboarding sequences. It simulates real-world user curiosity and error, providing a crucial layer of qualitative insight.
Tech leaders rely on this human-centric approach. Microsoft's internal teams have long used structured exploratory sessions to test new Windows features, uncovering usability issues that automated checks couldn't. Similarly, Spotify leverages exploratory testing to validate the end-to-end user experience, ensuring that new features not only function correctly but also feel intuitive and engaging to a diverse user base.
Key Insight: Exploratory testing is not random "ad-hoc" clicking. It is a structured and disciplined thought process, often managed through charters and time-boxed sessions, that focuses on learning and discovery rather than simple verification.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Integrating exploratory testing requires fostering a culture of curiosity and providing a structured framework. Here's how to begin:
- Implement Session-Based Test Management (SBTM): Structure exploratory efforts into time-boxed sessions (e.g., 60-90 minutes). Each session should have a clear charter or mission, outlining the area to be tested and the goals. Testers then document their findings, including bugs, questions, and notes on application behavior, in a concise session report.
- Focus on High-Risk Areas and User Personas: Direct exploratory efforts toward the most critical or complex areas of your B2B/SaaS platform. Use user personas to guide testing, asking questions like, "What would a sales manager trying to generate a report do here?" This context-driven approach helps uncover bugs that have a real impact on your target audience.
- Pair with Automation: Use exploratory testing to complement your automated test suite, not replace it. Automation is excellent for regression testing and verifying known paths, while exploration is ideal for discovering new, unknown risks. Findings from exploratory sessions can even inspire new automated test cases.
6. Cross-Functional Quality Teams
Cross-functional quality teams dismantle the traditional siloed QA department, embedding quality professionals directly into development pods. This modern approach redefines quality as a shared responsibility across all roles, including developers, product owners, designers, and testers. Instead of QA acting as a final gatekeeper, quality becomes an intrinsic part of the team's DNA, fostered through continuous collaboration and collective ownership.
This model accelerates feedback loops and enhances knowledge sharing. When a QA expert is part of the daily stand-ups, planning sessions, and retrospectives, potential issues are identified and addressed in real time. It cultivates a holistic understanding of the product, where every team member contributes to building quality from the ground up, aligning with core Agile and DevOps principles.

Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
In the fast-paced world of AI-driven B2B SaaS, isolated QA teams create bottlenecks that slow down innovation. A cross-functional structure ensures that quality considerations are baked into every decision, from initial UI/UX design to backend architecture. This is crucial for complex automation workflows, where a misunderstanding between development and QA can lead to critical failures in lead routing or data processing.
Spotify famously championed this model with its "squads," where each autonomous team has all the skills needed to deliver a feature, including quality assurance. This structure empowers them to move quickly while maintaining high standards. Similarly, tech retailer Shopify utilizes development pods with embedded quality-focused members to ensure their e-commerce platform remains robust and reliable, even as they rapidly deploy new features.
Key Insight: The goal of a cross-functional team isn't to eliminate dedicated QA roles but to amplify their impact. Embedded QA professionals become quality coaches, enabling the entire team to think critically about testing and risk.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Transitioning to a cross-functional model requires a cultural shift and clear operational guidelines. Here’s how to build one effectively:
- Define Clear Quality Roles and Responsibilities: Document who is responsible for what within the team. While everyone shares ownership of quality, the embedded QA expert might focus on test strategy and exploratory testing, while developers own unit and integration tests.
- Establish Shared Quality Goals and Metrics: Set team-wide objectives, such as reducing bug escape rates or improving test coverage. Track these metrics transparently to align everyone on a common definition of success and make quality a collective achievement.
- Foster a Culture of Open Communication: Implement regular quality-focused discussions in retrospectives to analyze what went well and what didn't. Encourage open feedback and create a psychologically safe environment where team members feel comfortable raising quality concerns. Learn more about how to improve your team's synergy with cross-functional collaboration.
7. Quality Metrics and KPIs
Quality metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the compass of your quality assurance best practices, providing objective, quantitative data to measure, monitor, and improve software quality. Instead of relying on gut feelings, this practice establishes a framework for data-driven decision-making, allowing teams to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and justify investments in quality initiatives. The core principle is "you can't improve what you don't measure."
By defining clear metrics, organizations can transform abstract goals like "improving quality" into tangible targets. These metrics provide a real-time view of the health of both the product and the development process, balancing leading indicators that predict future issues (e.g., code complexity) with lagging indicators that reflect past outcomes (e.g., number of production bugs).
Why It's a Top-Tier Practice
For AI-driven B2B and SaaS platforms, where uptime and reliability directly impact revenue, metrics are non-negotiable. Tracking KPIs like Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) or Customer Defect Rate helps quantify the user impact of quality issues and prioritize fixes. This data-centric approach ensures engineering efforts are aligned with critical business outcomes, preventing teams from wasting resources on low-impact activities.
Google’s DORA (DevOps Research and Assessment) metrics are a gold standard, focusing on four key indicators: deployment frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and time to restore service. Similarly, Amazon’s obsession with operational excellence is driven by a deep-seated culture of measurement, tracking everything from latency to error rates to ensure a seamless customer experience. These giants prove that systematic measurement is fundamental to building and maintaining high-quality software at scale.
Key Insight: Effective metrics are not about assigning blame or tracking vanity numbers. They are diagnostic tools that reveal systemic issues and guide process improvement, fostering a culture of continuous learning and accountability.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Implementing a metrics program requires careful planning to ensure you track what truly matters. Here’s how to get started:
- Align Metrics with Business Goals: Start by identifying your core business objectives (e.g., increasing user retention, reducing support tickets). Select KPIs that directly reflect these goals, such as Defect Escape Rate or Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores. This ensures your quality efforts demonstrably contribute to business success, a key step in measuring overall business growth.
- Automate Data Collection and Reporting: Manually tracking metrics is tedious and prone to error. Integrate your QA tools with platforms like Jira, Grafana, or a CI/CD dashboard to automate data collection. Create real-time, accessible dashboards that visualize trends and make the data easy for all stakeholders to understand.
- Balance Different Metric Categories: Create a balanced scorecard that includes metrics from various categories: process efficiency (e.g., test case execution rate), product stability (e.g., crash rate), performance (e.g., page load time), and security (e.g., vulnerability density). When defining performance indicators, you might even explore external Ruby on Rails performance services to benchmark and optimize specific application components.
Quality Assurance Best Practices Comparison
| Aspect | Shift-Left Testing | Risk-Based Testing | Test Automation Strategy | Continuous Testing | Exploratory Testing | Cross-Functional Quality Teams | Quality Metrics and KPIs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate – requires cultural/process changes and tooling setup | High – needs domain expertise and detailed risk assessment | High – involves tool selection, framework setup, and maintenance | High – requires robust CI/CD integration and infrastructure | Low to Moderate – depends on tester skill; less formal setup | Moderate – requires organizational and cultural changes | Moderate – requires metric selection, automation, and analysis |
| Resource Requirements | Additional tooling, training, and collaborative effort | Domain experts, stakeholder involvement, and planning time | Investment in automation tools, training, and ongoing maintenance | Infrastructure for automation and test execution; skilled engineers | Skilled testers with domain knowledge and time for investigation | Cross-training, leadership, and collaborative communication efforts | Tools for data collection, analysis, and stakeholder dashboards |
| Expected Outcomes | Early defect detection, reduced fix cost, faster feedback | Focused testing on high-risk areas, optimized resource use | Faster test execution, improved test coverage, ROI improvement | Immediate feedback, faster releases, maintained quality gates | Discovery of unexpected issues, improved UX insights | Enhanced collaboration, faster issue resolution, shared quality ownership | Data-driven quality insights, continuous improvement, informed decisions |
| Ideal Use Cases | Projects aiming to reduce defect cost early, improve code quality | Projects with limited testing resources, high-risk critical systems | Organizations scaling automated tests for faster CI/CD | Teams practicing DevOps and Agile with CI/CD pipelines | Projects needing human intuition to find unknown issues | Agile teams wanting shared quality responsibility and collaboration | Organizations seeking measurable quality performance and trend analysis |
| Key Advantages | Cost savings on defect fixes, improved collaboration, faster delivery | Maximizes test efficiency, stakeholder alignment, focused coverage | High test reliability, repeatability, and scalable testing | Continuous quality assurance, faster releases, DevOps support | Flexibility, adaptability, uncovering hard-to-find bugs | Strong team cohesion, reduced delays, collective ownership | Objective measurement, trend identification, supports resource decisions |
Building a Future-Proof Quality Culture
The journey through these seven quality assurance best practices reveals a powerful, interconnected truth: quality is not a final checkpoint, but a continuous, cultural commitment. Moving beyond siloed testing departments and last-minute bug fixes is the definitive leap from a reactive startup to a proactive, scalable B2B SaaS leader. The strategies we have explored, from shifting left to implementing risk-based analysis, are not just isolated tactics; they are the foundational pillars of an organization engineered for excellence.
When you integrate a robust test automation strategy and embrace continuous testing, you transform your development pipeline from a bottleneck into a high-speed-delivery engine. This momentum, however, must be balanced with the creative, human-centric approach of exploratory testing. This combination of structured automation and unscripted investigation ensures you catch both predictable failures and unexpected user-experience flaws, delivering a product that is not only functional but truly delightful to use.
From Process to Culture: The Human Element
Perhaps the most critical takeaway is the shift from process to culture. Establishing cross-functional quality teams breaks down the "us vs. them" mentality that often plagues development and QA relationships. When developers, product managers, and testers share ownership of quality, everyone is invested in the outcome. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and accountability, turning quality from a department’s responsibility into a company-wide value.
To sustain this culture, you need a clear line of sight into what is working and what is not. This is where quality metrics and KPIs become indispensable. They provide the objective data needed to move beyond guesswork, enabling you to:
- Identify bottlenecks in your development and testing cycles.
- Measure the impact of new processes and tools.
- Justify investments in quality-focused initiatives.
- Align team efforts with overarching business goals like customer retention and satisfaction.
Without these metrics, even the best-intentioned efforts can feel directionless. They are the compass that guides your continuous improvement journey. For a comprehensive understanding of foundational QA, explore this detailed guide on software quality assurance processes which provides an excellent framework for building these systems from the ground up.
Your Actionable Path Forward
Adopting these quality assurance best practices is not an overnight transformation but a series of deliberate, strategic steps. The goal is to build a resilient operational DNA that embeds quality into every workflow, every decision, and every line of code. By doing so, you are not just preventing bugs; you are building customer trust, protecting your brand reputation, and creating a sustainable competitive advantage in the crowded SaaS marketplace. This is how you future-proof your business against the complexities of scale and the rising expectations of your clients.
The ultimate value lies in creating a system where quality is so deeply integrated that it becomes an invisible, yet powerful, force driving your growth. It frees your team from constant fire-fighting, allowing them to focus on innovation and delivering exceptional value. This is the true hallmark of a mature, quality-driven organization.
Ready to embed these quality principles directly into your automated workflows? MakeAutomation specializes in building and optimizing the very systems discussed in this article, ensuring your automations are robust, reliable, and scalable from day one. Visit MakeAutomation to see how we can help you build a culture of quality that accelerates your growth.