DevOps Life Cycle: Master Each Stage – devops life cycle insights for SaaS
The DevOps life cycle isn't just another industry buzzword; it's a fundamental shift in how we build and deliver software. Think of it as a continuous, looping process that brings software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) together. The goal? To knock down the walls between these traditionally separate teams, speed up the entire development timeline, and consistently ship high-quality software.
This approach replaces the old, clunky, siloed way of doing things with a collaborative loop of planning, coding, testing, and monitoring that never really stops. For any business trying to get products to market faster while keeping everything stable, this framework is a game-changer.
Why the DevOps Life Cycle Matters for Growth
Picture your software development process as a clumsy relay race. Developers write some code and toss it over the wall to testers, who eventually pass it on to the operations team. Every handoff is a chance for delays, miscommunication, and dropped batons.
Now, imagine a Formula 1 pit crew. Everyone works in perfect sync, a blur of focused, coordinated action. That’s what a solid DevOps life cycle brings to the table. It transforms those disjointed handoffs into a seamless, high-velocity workflow.
This isn’t just a technical to-do list; it's a strategic blueprint for scalable growth. By merging these once-separate functions, you create a powerful feedback loop where insights from the live product in operations feed directly back into the next development cycle.
The Business Impact of Adopting DevOps
For a B2B or SaaS company in a growth phase, this integrated approach is a serious competitive edge. The proof is in the numbers. The DevOps market is expected to explode from $10.4 billion in 2023 to $25.5 billion by 2028.
This isn't just hype. A staggering 99% of organizations see positive results from their DevOps initiatives, and on average, they cut their time-to-market by 49%. You can explore more of these trends with these key DevOps statistics.
Ultimately, this framework is about breaking down bottlenecks, building more resilient systems, and delivering value to your customers faster. If you want to dig deeper into the core ideas, understanding What Is DevOps Methodology is a great place to start.
Adopting the DevOps life cycle is about transforming your entire value stream, from initial idea to live production, into an efficient, predictable, and scalable engine for growth.
A High-Level Overview of the Stages
The process is generally mapped out across eight distinct but deeply connected stages, each one feeding into the next. It’s a continuous cycle designed to ensure teams are always improving, innovating, and responding to business needs with real agility. Embracing this mindset is a huge part of a company's overall evolution, a topic we cover in our guide on https://makeautomation.co/what-is-digital-transformation/.
To give you a clear roadmap of what's to come, here’s a quick summary of the eight stages we'll be breaking down.
The 8 Stages of the DevOps Life Cycle at a Glance
| Stage | Primary Goal |
|---|---|
| 1. Plan | Define business requirements, features, and the project roadmap. |
| 2. Code | Develop the software and manage changes with version control. |
| 3. Build | Compile source code into a runnable application artifact. |
| 4. Test | Automate testing to validate code quality and find bugs early. |
| 5. Release | Prepare the build artifact for its journey to production. |
| 6. Deploy | Push the release into the live production environment. |
| 7. Operate | Keep the application running smoothly for end-users. |
| 8. Monitor | Collect performance data and feedback to inform the next cycle. |
Each of these stages plays a critical role in creating that seamless, automated workflow we’re aiming for. Let's dive into each one.
A Stage-by-Stage Breakdown of the DevOps Workflow
Forget rigid, linear checklists. The DevOps life cycle is a fluid, continuous loop built for speed and quality. Think of it as an infinity symbol: insights from the very last stage immediately feed back into the first, creating a system that gets smarter with every cycle. Each stage has its own job, but the real magic happens in how seamlessly they all connect.
This interconnected flow is often boiled down to a simple "Develop, Deploy, and Monitor" loop, which captures the core rhythm of DevOps.
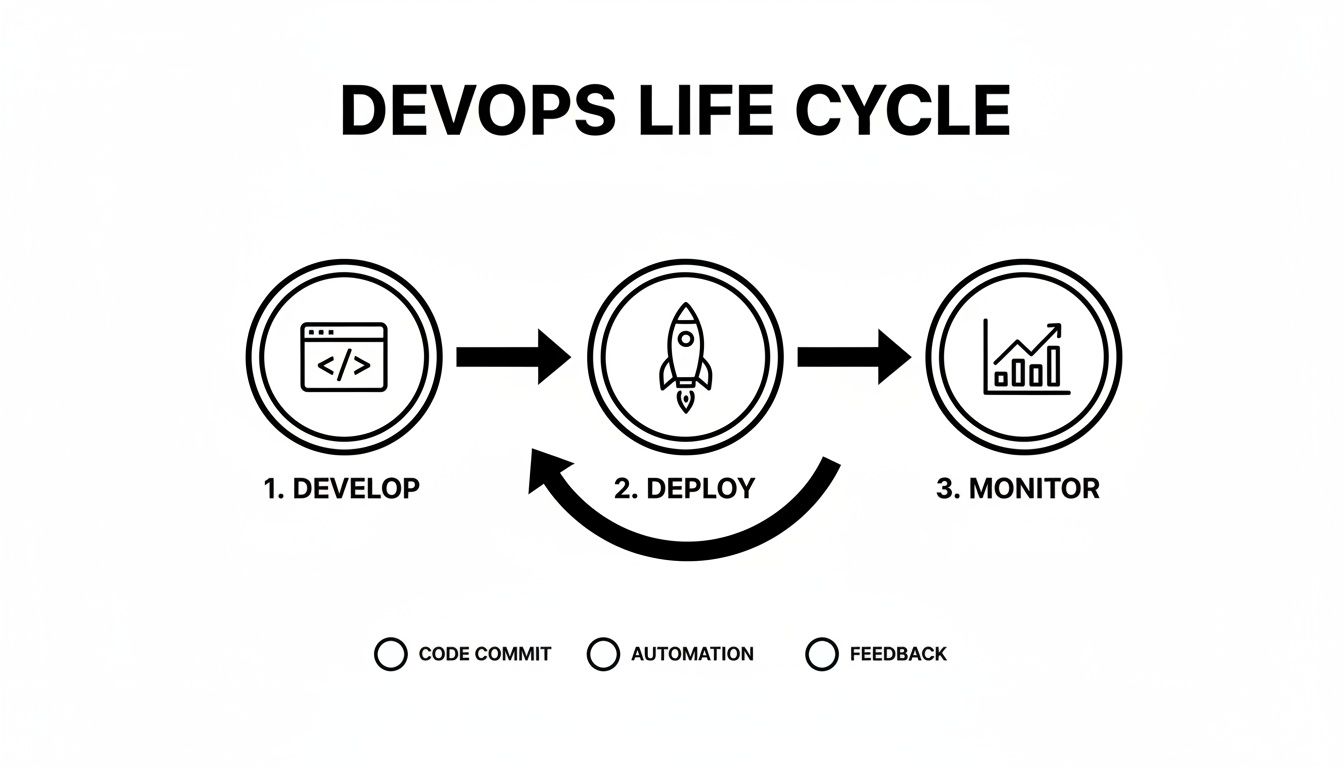
This graphic shows how development naturally flows into deployment, which in turn feeds the monitoring process. That constant stream of feedback is what drives real, continuous improvement. Now, let’s unpack the eight stages that make this high-velocity workflow a reality.
Stage 1: Plan
Before anyone writes a single line of code, the journey starts with a solid plan. This is where we figure out what we’re building, why we’re building it, and what success looks like. Product managers, analysts, and team leads get together to hash out requirements, prioritize features, and sketch out a project roadmap.
The main goal here is to create a crystal-clear, shared understanding of the mission. It’s less about technical details and more about aligning the team's effort with the bigger business goals.
- Who's Involved: Product Managers, Business Analysts, Project Managers, Team Leads.
- Key Activities: Gathering requirements, prioritizing features, creating user stories, and planning sprints.
- Example Tools: Jira, Trello, Asana, Monday.com.
Stage 2: Code
With a plan in hand, developers fire up their IDEs. The "Code" stage is where the software actually gets written. But in a DevOps world, it’s not just about cranking out features. It’s about writing code collaboratively and maintaining a single source of truth for the entire project.
This is where version control systems like Git become non-negotiable. Every change, no matter how small, is tracked, committed to a shared repository, and reviewed by another developer. This simple habit prevents code conflicts and ensures everyone is building from the same, up-to-date foundation.
- Who's Involved: Software Developers, DevOps Engineers.
- Key Activities: Writing code, conducting peer code reviews, merging feature branches, and managing source code.
- Example Tools: Git, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, VS Code.
Stage 3: Build
As soon as a developer commits their code, the "Build" stage automatically kicks in. This is the first taste of true automation in the DevOps life cycle. The source code is compiled into a runnable artifact—an executable file or package ready for deployment. This whole process is orchestrated by a continuous integration (CI) server.
Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of automatically building and testing code every time a team member commits a change. This automation is a safety net that catches integration bugs early, when they're still small and easy to fix.
The CI server grabs the latest code, compiles it, and runs some basic checks. If the build fails for any reason, the team gets an immediate alert, allowing them to jump on the problem before it snowballs.
Stage 4: Test
Just because the code compiles doesn't mean it works. The "Test" stage is where the build artifact gets put through its paces with a battery of automated tests to hunt down bugs and confirm it works as intended. This is a critical quality gate in the pipeline.
Quality Assurance (QA) engineers design and manage suites of automated tests that cover everything from tiny code snippets to the application as a whole.
- Unit Tests: Check that individual functions or components work in isolation.
- Integration Tests: Make sure different modules and services can talk to each other correctly.
- User Acceptance Tests (UAT): Confirm that the software meets the business requirements from an end-user's perspective.
This heavy automation lets teams test constantly and thoroughly without slowing down the pace of releases. Tools like Selenium, JUnit, and Cypress are workhorses in this phase.
Stage 5: Release
Once the build has passed all its tests, it's officially considered ready for production. The "Release" stage is all about packaging that artifact and preparing it for deployment. This is an orchestration step where the team finalizes release notes, applies any last-minute configurations, and stores the final build in a repository.
Think of it as the final pre-flight check before launch. A release manager or DevOps engineer typically oversees this stage, ensuring every dependency is accounted for and the release is properly versioned.
Stage 6: Deploy
Deployment is where the rubber meets the road. This is the moment the release artifact is pushed into the live production environment, making it available to your users. Modern DevOps teams lean on automated, low-risk deployment strategies to avoid downtime and drama.
This automated push to production is a cornerstone of Continuous Delivery. To go deeper on this, check out our guide on DevOps and Continuous Delivery.
Some of the most common deployment strategies include:
- Blue-Green Deployment: You run two identical production environments ("Blue" and "Green"). The new release goes to the inactive one. Once it's tested and looks good, you simply switch the traffic over.
- Canary Release: The new version is rolled out to a tiny fraction of users first. If all goes well, you gradually roll it out to everyone else.
Tools like Ansible, Chef, Puppet, and container platforms like Kubernetes are essential for making deployments repeatable and reliable.
Stage 7: Operate
The software is live—but the job isn't done. The "Operate" stage is all about managing and maintaining the application in production. This used to be the sole responsibility of the operations team, but in DevOps, developers share in this ownership.
Activities here include managing infrastructure, patching security vulnerabilities, scaling resources up or down to meet demand, and handling data backups. The goal is to keep the application running smoothly, securely, and efficiently.
Stage 8: Monitor
The final stage, "Monitor," brings everything full circle. Here, teams constantly collect performance data and user feedback from the live application. This isn't about waiting for things to break; it's about being proactive. Monitoring tools track everything from CPU usage and server latency to application errors and user behavior patterns.
The insights you gather here are pure gold. They help you find bugs you didn't know you had, pinpoint performance bottlenecks, and see how people are actually using your new features. This data flows directly back into the "Plan" stage, kickstarting the next cycle and ensuring the DevOps life cycle is a true engine of continuous improvement.
Integrating Security into Every Stage with DevSecOps
In the old way of building software, security was an afterthought. Imagine an entire car being built, painted, and polished before anyone bothered to check if the locks worked. If a flaw was found, the car had to be sent all the way back down the assembly line, creating huge delays and headaches. That last-minute inspection model just doesn't fly in the world of SaaS.
For any B2B company, a security breach isn't a simple IT ticket—it's a potential catastrophe that can shatter customer trust overnight. This is why the DevOps life cycle needs to evolve into DevSecOps. The core principle is simple but incredibly effective: shift security left. Instead of bolting security on at the end, you weave it into every stage of the process, right from the very beginning.

This shift makes security a shared responsibility. It's no longer just the security team's problem. Developers, operations pros, and security experts all work together, making the entire pipeline stronger and more resilient from the ground up.
Embedding Security into the Workflow
The goal here isn't to add more manual hurdles that slow everyone down. It's about automating security checks directly into your CI/CD pipeline. When you do this, you create a system that catches vulnerabilities early and automatically, long before they have a chance to hit a live server.
Here's how security fits into a few key stages:
- Code Stage: Developers can use Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools that scan code for common vulnerabilities as it's being written. Think of it like a spell checker for security holes, giving immediate feedback right inside the developer's editor.
- Build Stage: As the code is compiled, automated scans can check all third-party libraries and dependencies for known security flaws. This simple step prevents your application from inheriting problems from outside code.
- Test Stage: During automated testing, Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools get to work. They actively probe the running application, simulating real-world attacks in a safe environment to find weaknesses that only appear at runtime.
By making security an automated, everyday part of the workflow, you build a culture where everyone thinks about security. It's a proactive stance that's far more effective—and much less expensive—than cleaning up after a breach. Mastering modern application security best practices is key to making this proactive approach a reality.
The Business Case for DevSecOps
Let's be clear: adopting a DevSecOps mindset isn't just a technical upgrade; it's a business necessity. The market for DevSecOps is expected to explode from $3.73 billion in 2021 to a staggering $41.66 billion by 2030. Why? Because the average cost of a data breach is now over $10 million. The numbers speak for themselves.
DevSecOps transforms security from a bottleneck into a business accelerator. By catching and fixing vulnerabilities early, you not only protect your customers but also increase your release velocity and build a more trustworthy, resilient product.
Teams that integrate security from the start can deploy software on demand and recover from incidents in less than an hour. That’s a massive competitive advantage.
This approach ensures security and quality assurance are two sides of the same coin. If you're looking to strengthen that link, our guide on quality assurance best practices is a great place to start. In the end, baking security into the DevOps life cycle provides something invaluable: peace of mind for your customers, your stakeholders, and your own team.
Building Your Modern DevOps Toolchain
A successful DevOps life cycle isn't just about a new mindset; it's a well-oiled machine powered by a stack of integrated tools. Think of it like building a high-performance car. You can have the best engine, transmission, and suspension, but they're useless unless they work together perfectly. Your DevOps toolchain is no different—it’s about connecting various technologies to automate and smooth out the entire software delivery process.
The real aim isn't just to collect a bunch of tools. It's to create a seamless, automated workflow. This connected chain of tools creates what's known as a CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) pipeline. This pipeline is the automated superhighway that moves code from a developer's laptop to a live production environment with as little human meddling as possible.
Connecting The Stages With Technology
Every stage in the DevOps life cycle has a specific job to do, and there are tools built to master each one. The magic happens when you get these tools talking to each other. For instance, a simple code commit in Git should instantly trigger a new build in Jenkins, which in turn kicks off a full suite of automated tests in a tool like Selenium.
If any single step fails, the entire pipeline halts and immediately alerts the team. This instant feedback loop is what makes DevOps so powerful for maintaining both speed and quality. It guarantees that problems are caught and fixed right away, back when they’re still small and cheap to solve.
This diagram from Wikipedia does a great job of showing how different tools fit together to cover the entire DevOps loop.
You can see how the process flows continuously, with specific functions like "Code," "Build," and "Test" all interconnected in an endless cycle.
Core Components of a Modern Toolchain
You don’t need to go out and buy a massive, all-in-one platform to get started. Most growing companies begin with a few core tools and build out their stack over time. The trick is to pick technologies that play well together and support the collaborative culture you’re aiming for.
Here are the essential tool categories you’ll want to cover:
- Planning and Collaboration: This is your project’s command center, where teams define tasks, track what’s getting done, and manage the product backlog.
- Source Code Management: A version control system is completely non-negotiable. It’s the single source of truth for every line of code your team writes.
- Build and Integration: These are the automation engines that compile code and run initial sanity checks every single time a developer pushes a change.
- Testing Automation: Frameworks that run a battery of tests—functional, performance, security—automatically, so you can validate quality without manual drudgery.
- Deployment and Configuration: Tools that automate pushing code to your servers and ensure every environment is configured exactly the same way.
- Monitoring and Observability: Solutions that keep an eye on your live applications, collecting performance data and logs to give you real-time insights and alerts.
A well-designed toolchain does more than just automate tasks. It becomes the shared workspace where developers and operations teams truly collaborate, creating a transparent, repeatable, and reliable process for shipping great software.
Choosing the right tools is a huge step in making the DevOps life cycle a reality for your team. To give you a better idea of what this looks like in practice, the table below maps popular tools to each stage of the life cycle.
Example DevOps Toolchain by Life Cycle Stage
| Stage | Example Tools | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Plan | Jira, Trello, Asana | Track user stories, manage sprints, and visualize project roadmaps. |
| Code | Git, GitHub, GitLab | Manage source code versions, facilitate code reviews, and store repositories. |
| Build | Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI | Automate the compilation of source code into a runnable application artifact. |
| Test | Selenium, JUnit, Cypress | Run automated tests to validate functionality, performance, and security. |
| Release | Docker, Artifactory | Package the application into containers and manage release artifacts. |
| Deploy | Ansible, Kubernetes, Terraform | Automate the deployment of applications to production environments. |
| Operate | Chef, Puppet, SaltStack | Manage and configure infrastructure to ensure stability and consistency. |
| Monitor | Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog | Collect metrics, logs, and traces to observe application performance and health. |
Think of this table as a blueprint. You can mix and match these tools to build a technology stack that fits your team's specific needs and budget.
Bringing AI and Automation into Your DevOps Life Cycle
Once you have a solid DevOps life cycle running, the next step isn't just to make it faster—it's to make it smarter. This is where artificial intelligence and intelligent automation enter the picture, turning a well-oiled machine into a self-optimizing engine for growth. We're moving beyond simple scripts that automate repetitive tasks and into a world where predictive power gets baked into every stage of the cycle.
This shift is most apparent in a practice called AIOps, which stands for AI for IT Operations. Think of AIOps as a brilliant co-pilot constantly watching over your live systems. It digs through the mountains of data generated during the 'Operate' and 'Monitor' phases, searching for faint signals that whisper of trouble on the horizon.

AIOps: Predicting Problems Before They Start
Traditional monitoring tools are reactive; they sound the alarm after something has already broken. AIOps flips the script by aiming to predict failures before they ever impact a user. It does this by learning from historical performance data and analyzing real-time metrics, spotting tiny anomalies that a human operator would almost certainly miss.
A classic example is a slow memory leak that won't cause an outage for days. An AIOps system can flag this subtle deviation and then automatically trigger a fix, like restarting a specific service during a low-traffic window. Just like that, potential downtime is avoided entirely. This proactive stance transforms operations from a constant firefight into a more strategic, predictive discipline.
This isn't just a niche trend. An estimated 73% of enterprises are expected to adopt AIOps to keep up with the data explosion from modern apps, with experts bluntly stating there's "no future of IT operations without AIOps." It makes sense, too—mature DevOps teams already dedicate 33% more time to improving infrastructure, and AI ensures that time is spent on high-impact work. You can explore more of these essential DevOps trends and strategies to stay ahead.
Smart Automation Earlier in the Cycle
But AI's influence doesn't stop at operations. Intelligent tools are now popping up much earlier in the DevOps life cycle, giving developers and QA engineers superpowers to focus on creative problem-solving instead of tedious, repetitive work.
Here’s how it’s changing the game:
- AI-Assisted Coding: Tools built right into the developer's editor can now suggest code snippets, spot bugs as they're typed, and even write entire functions from a plain-English prompt. This not only saves time but also helps maintain consistent coding standards across the team.
- Automated Test Case Generation: Instead of manually writing test scripts, AI can analyze a new feature and automatically generate a robust suite of tests to cover it. This is a massive time-saver for QA teams, allowing them to ship with confidence without slowing down.
- Smart Code Reviews: Before a pull request even reaches a human reviewer, AI can perform a first pass. It checks for common mistakes, security vulnerabilities, and style guide violations, catching the low-hanging fruit so engineers can focus on the architectural big picture.
By weaving AI into your workflow, you create a powerful feedback loop. Insights from production data automatically feed back to inform and improve the very next development cycle. This is how you turn your DevOps pipeline into a genuine competitive advantage.
At the end of the day, bringing AI and sophisticated automation into your process is about more than just efficiency. It’s about building a smarter, more resilient, and far more responsive system for delivering real value to your customers.
Got Questions About the DevOps Life Cycle? We've Got Answers.
Jumping into a new way of working is always going to bring up questions, and the DevOps life cycle is no different. If you're running a B2B or SaaS company, figuring out the real-world implications is the key to making the switch stick. Let's tackle the most common questions head-on to help you navigate the process, avoid the usual traps, and actually measure what success looks like.
Remember, this isn't just a tech upgrade. It's about getting your engineering engine perfectly in sync with your business goals. Nailing the basics from day one will make the entire journey smoother and far more effective for everyone involved.
How Is the DevOps Life Cycle Different from Agile?
This is easily the most common point of confusion, but the difference is pretty simple once you see where each one focuses. They aren’t competing philosophies; they're partners that solve different parts of the same delivery puzzle.
Think of it like this: Agile is a project management mindset focused on the planning and coding parts of building software. It’s all about breaking down big, intimidating projects into small, digestible sprints. This lets your team adapt to new information and ship features piece by piece. Agile's main job is to help you decide what to build and in what order.
The DevOps life cycle, on the other hand, stretches that same collaborative thinking across the entire process. It takes the fast, iterative spirit of Agile and applies it all the way from the first commit to monitoring the app running in front of customers. DevOps is all about how you deliver, operate, and support that software reliably as you grow.
Agile helps you finish a feature faster. DevOps gets that finished feature to your customers faster—and more safely. Put them together, and you have a powerhouse system for shipping value without the drama.
What Are the Most Common Pitfalls When Adopting DevOps?
Lots of teams stumble when they try to adopt DevOps, and it’s almost never about the technology itself. The single biggest mistake is getting obsessed with tools while completely ignoring the cultural shift required. Simply buying a new CI/CD platform won't magically make your teams collaborate.
A real transition means deliberately tearing down the walls that traditionally separate developers from operations. It’s about creating an environment of shared ownership, constant communication, and mutual respect.
Here are a few other traps to keep on your radar:
- No Leadership Buy-In: If management isn't championing the change, a DevOps initiative is dead in the water. Leaders have to not only approve it but also provide the team with the time and resources to do it right.
- Forgetting About Security: Trying to bolt on security at the very end is a recipe for disaster. When you don't build security into the process from the start (often called DevSecOps), you introduce massive risks and slow everything down.
- Not Measuring Anything: You can't improve what you don't measure. Too many teams dive in without defining what success even looks like, making it impossible to show the ROI of their efforts later on.
How Can a Small SaaS Startup Begin Implementing DevOps?
You absolutely do not need a huge team or a massive budget to get started with the DevOps life cycle. For a small SaaS startup, the secret is to start with the basics that give you an immediate win. Automate one small thing, prove its value, and build momentum from there.
A practical, step-by-step approach is always the best bet. Your goal is to create a solid foundation you can add to as your team and product get more complex.
Here's a simple, four-step roadmap to get you going:
- Get Everything in Version Control: This is non-negotiable. Put all your application code, infrastructure configs, and deployment scripts into a version control system like Git. This establishes a single source of truth for everything you build and run.
- Set Up a Basic CI/CD Pipeline: Next, automate your build and test process. The goal is to have a simple pipeline that automatically runs every time a developer commits new code. This is your first and most important safety net.
- Automate Your First Deployment: With builds and tests automated, take the leap and automate deployment to a staging environment. This gets rid of risky manual steps and dramatically cuts down on "it worked on my machine" problems.
- Add Basic Monitoring: Finally, close the loop. Put some simple monitoring and alerting in place for your production app. This gives you instant feedback on the impact of your changes and helps you jump on issues before customers even notice.
What Key Metrics Should We Track to Measure DevOps Success?
To justify your investment and guide your improvements, you need to track the metrics that actually matter. The industry has largely settled on a core set of four, famously known as the DORA metrics (from the DevOps Research and Assessment team).
These four KPIs give you a balanced, high-level view of your software delivery performance, covering both speed and stability. They help you answer the two most important questions: How fast can we ship value, and how reliable is our process?
Focus your efforts on tracking these four:
- Deployment Frequency: How often do you successfully release code to production? Elite teams do this on-demand, often many times per day.
- Lead Time for Changes: How long does it take for a code commit to make it all the way to production? This is a pure measure of your team's velocity.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): When something breaks in production, how long does it take you to fix it? This is a crucial indicator of your team's resilience.
- Change Failure Rate: What percentage of your deployments cause a production failure that requires a fix (like a rollback or a patch)? This tells you a lot about your overall quality and stability.
By keeping a close eye on these four metrics, you'll get a clear, data-driven picture of your performance and know exactly where to focus your efforts to improve your DevOps life cycle.
Ready to eliminate costly manual workflows and accelerate your growth? MakeAutomation specializes in implementing the AI and automation frameworks that power a modern DevOps life cycle, helping B2B and SaaS businesses scale efficiently. Optimize your operations with MakeAutomation.